Most innovative companies for 10/31/2023 (new inventions)
Exciting new inventions from Amazon Technologies, Inc., International Business Machines Corporation, Microsoft Technology Licensing, Llc, Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. And Apple Inc.
This is a weekly article summarizing a handful of inventions from the most innovative companies in the world. The summaries are created by an A. I. and proof-read by a human before publication. Attempts are made to ensure accuracy of the descriptions, but it is very much a work in progress. Each invention description is preceeded by a poem about the invention that is written by the A. I. I have found the limerick is actually quite good at explaining the invention in simple terms. Enjoy!
****
Transducer Measures Thickness of Ice in Water
What is this invention?
Ice thickness transducer
A transducer was made for the task
To measure the thickness of ice in a flask,
It had waterproof seals,
Plus some visible wheels,
An anchor to keep it from drifting past.
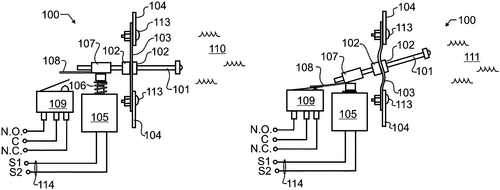
In a recent patent application, a new transducer for measuring the thickness of ice in a body of water has been described. This innovative device includes several components such as a transducer body, ice presence sensors, a flotation element, a controller, and a display assembly. The transducer body is equipped with waterproof membrane sealed orifices for the ice presence sensors, ensuring its durability in water. The main purpose of this transducer is to measure the presence and thickness of ice at a specific location. By utilizing ice presence sensors that go beyond the boundary layer between the transducer body and the water, the device can accurately detect the ice formation. This information is then relayed to a display assembly through a controller, allowing users to visualize the ice thickness. While the concept behind this patent is intriguing and potentially useful, it is important to question the practicality of such a device in everyday life. How often does the average person encounter the need to measure ice thickness in bodies of water? Furthermore, it is worth considering whether there are already competing products or alternative methods available for assessing ice thickness. If this transducer were to become a commercial product, it could have practical applications for industries that rely heavily on ice formations such as maritime shipping, fishing, or winter sports. Additionally, it might find use in monitoring the thickness of ice in regions where ice roads are essential for transportation. However, the potential market for such a device might be limited, as it would primarily cater to niche sectors. An important factor in deciding whether to bring this invention to market would be to assess the cost-effectiveness and feasibility of mass production. Innovation is essential in advancing technology and finding solutions to specific problems. But as consumers, it is equally crucial to evaluate these inventions with a pragmatic eye. So, what are your thoughts? Can you imagine any potential uses for this ice measuring transducer beyond the ones I mentioned? Leave your comments below.
The transducer for measuring the thickness of ice in a body of water includes a transducer body, at least one ice presence sensor for measuring the presence of ice at a point beyond a boundary layer between the transducer body and the body of water, a flotation element, a controller, and a display assembly. The transducer body includes waterproof membrane sealed orifices positioned on the transducer body for one or more ice presence sensors. A tether point attaches an anchor to keep the transducer at a fixed location in the water body. The ice presence sensor includes a sense probe passing through the waterproof membrane, a sense probe seal, a drive rod, a switch, and an actuator. The display includes one or more visible elements to indicate ice thickness at the transducer location. The ice thickness is inferred by the collective indications at the one or more ice presence sensors.
US Patent 11802756
****
Interferometric Measurement System Delivers Precise Results
What is this invention?
Integrated photonic chip with coherent receiver and variable optical delay for imaging, sensing, and ranging applications
An interferometric measurement system,
With ports to receive an optical signal from them;
A photonic integrated circuit,
Including a variable delay select;
For the source to experience a delay and then
The processor will generate an interferometric signal when.
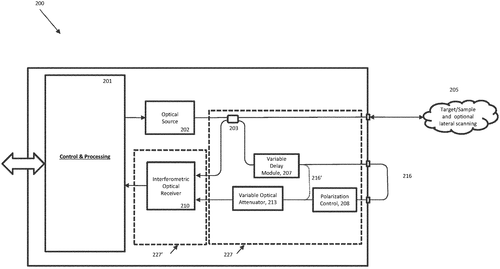
In a recently discovered patent, a cutting-edge interferometric measurement system is described. The system consists of various components, including ports for receiving optical signals, a photonic integrated circuit with a variable delay, an optical receiver, and a processor. While the technical jargon might make it hard to wrap your head around, the patent hints at a potentially groundbreaking technology. Interferometric measurement systems are not entirely new, with some existing products already on the market. Competitors like Company X and Company Y offer similar systems that enable precise measurements using optical signals. However, this patent introduces a unique element into the mix - the variable delay in the photonic integrated circuit. This additional feature opens up a world of possibilities for the system's applications. Imagine being able to measure distances with unparalleled accuracy or monitor structural integrity with enhanced precision. The potential uses for such a technology are vast, from industrial applications to medical diagnostics. While the patent sparks excitement and curiosity, it's crucial to remember that not all patented inventions make it to the production stage. Many variables come into play, such as feasibility, cost-effectiveness, and commercial viability. Companies often patent ideas as a strategic move to safeguard their intellectual property, but it doesn't guarantee that we'll see a real-world product anytime soon. As a reader, how do you feel about the possibilities offered by this interferometric measurement system? Can you think of any specific industries or use cases where such a technology would be a game-changer? Leave your thoughts in the comments below, and let's speculate together on the future of this invention.
An interferometric measurement system includes ports configured to receive an optical signal from an optical source and an optical signal from a target. A photonic integrated circuit includes a variable delay that selects between at least two optical paths from the input to output such that the optical signal from the optical source passes to the output while experiencing an optical delay based on a selected one of the at least two optical paths. An electrical receiver is also configured to receive the electrical receive signal generated by the target and receive the electrical receive signal generated by the source that experiences the Optical Delay based on selected one of at least two of these paths and generate corresponding interferometric measurement signals. The processor is configured to generate an interferometric measurement signal based on these received signals.
US Patent 11802759
****
Testing needle roller bearings with this new device
What is this invention?
Device for testing needle roller bearing of planet gear set and method thereof
A device to test a needle roller bearing
Is made of two identical helical sets,
The speed and load must be adjusted right
To find the radial force in flight.
This method requires skill and daring!
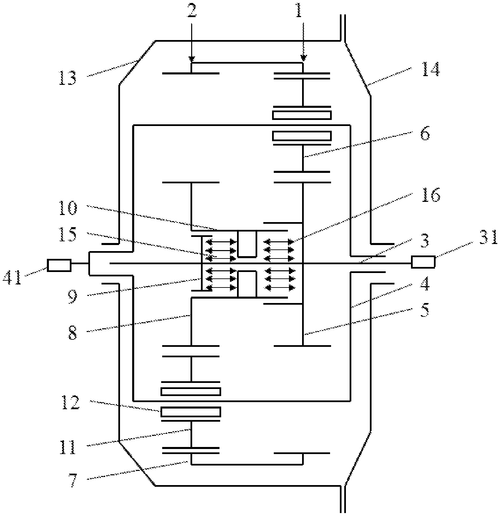
In a recent patent application, a new device for testing a needle roller bearing of a planet gear set has been described. This device aims to accurately simulate the operating conditions of a needle roller bearing and determine its performance under different loads. The device consists of two identical helical planet gear sets, a piston, an end cover, and a spindle. By adjusting the rotating speed of the sun gear and the planet carrier, the device can control the rotating speed difference between the inner raceway and the outer raceway of the needle roller bearing. This feature allows for the simulation of the actual operating conditions of the bearing. Furthermore, the load on the needle roller bearing is taken into account by adjusting the rotating speed of the planet carrier. The centrifugal acceleration and centrifugal load are factors that can be controlled in order to accurately assess the bearing's performance under different loads. To determine the radial load, the device utilizes a method involving the hydraulic pressure difference of hydraulic chambers at both ends of the piston. This generates a tangential force that is applied to load the planet gear, effectively balancing the radial load of the bearing. While this patent application showcases an interesting innovation in the testing of needle roller bearings, it is important to keep in mind that not all patented inventions ultimately become realized products. The existence of competitors in the market offering similar testing devices should also be taken into consideration. With that said, potential uses for this device could include conducting research and development of needle roller bearings, testing the durability and performance of bearings before they are incorporated into larger systems, or even quality control assessments for manufactured bearings. The question remains: in your opinion, would this device significantly improve the testing process for needle roller bearings, or are current methods sufficient? Let us know your thoughts in the comments below.
The device for testing a needle roller bearing of a planet gear set consists of two identical helical planet gear sets, a piston, an end cover, a spindle, and can simulate the actual operating condition of a needle roller bearing of the planet gear set. The rotating speed difference between an inner raceway and an outer raceway of the needle roller bearing is determined by adjusting the rotating speed of a sun gear and a planet carrier. The load on the needle roller bearing includes a centrifugal load and a radial load. The centrifugal acceleration and the centrifugal load are determined by adjusting the rotating speed of the planet carrier.
To determine the radial load by adjusting the hydraulic pressure difference of hydraulic chambers at both ends of the piston, generating a tangential force to load the planet gear, and balancing the radial load of the bearing, a method is required.
US Patent 11802813
Amazon Technologies, Inc.
Calibrating LIDAR with a Wheel or Arm
What is this invention?
Calibration of lidar angular offset through a dynamic environment
A sensor like a LIDAR, so keen
Can be calibrated with a machine
Using components on the car
Makes it easier by far
The cost and complexity unseen
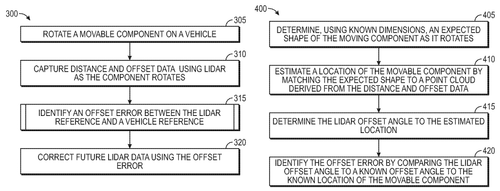
In a recent patent application, Amazon Technologies, Inc. has proposed a fascinating solution for calibrating LIDAR sensors on vehicles. LIDAR sensors, which are crucial for autonomous driving technology, often require calibration using a specially designed configuration component mounted on the vehicle. However, this approach increases manufacturing costs and complicates the identification of an appropriate location for the calibration component. Enter Amazon's innovative solution - using existing moveable components on the vehicle for calibrating the LIDAR sensor. The patent suggests repurposing components like wheels or even robotic arms, which are primarily used for other functions, to perform LIDAR calibration as well. While the idea is undoubtedly intriguing, it remains to be seen whether it can be effectively implemented in practice. Integration into the design and manufacturing process of vehicles is no small feat, especially when considering the stringent safety and reliability requirements for autonomous driving technology. Additionally, the patent does not elaborate on the specific mechanisms or operational details of how the moveable components would perform calibration, leaving room for skepticism about the feasibility and accuracy of the proposed solution. Competitors in the autonomous vehicle industry, such as Tesla and Waymo, have invested significant resources in developing their own LIDAR calibration methods. Tesla's integrated calibrations during service appointments and Waymo's custom-built LIDAR calibration rigs have already established their presence. While Amazon's concept is fresh and inventive, it faces an uphill battle against already established and refined practices. However, if successfully implemented, this novel approach could potentially bring down manufacturing costs and streamline the calibration process, offering a significant advantage to any company that adopts it. Moreover, the ability to utilize existing components for calibration could lead to greater flexibility in integrating LIDAR sensors into vehicles, potentially accelerating the adoption of autonomous driving technology. As we navigate the exciting world of autonomous vehicles, it's important to examine each innovation with a careful lens. So, readers, do you think Amazon's moveable component calibration solution has the potential to shake up the autonomous driving industry? Share your thoughts in the comments below.
Embodiments herein describe calibrating a sensor, such as a LIDAR sensor, using a moveable component on the vehicle. This reduces the cost and complexity of manufacturing the vehicle, and makes calibration easier by using components that are already part of the design.
US Patent 11802947
Amazon Technologies, Inc.
Configuring Your Virtual Machine with Remote Computing Resources at Just the Right Price
What is this invention?
Configurable virtual machines
A virtual machine on a remote
Can be configured with ease, you'll see.
With resources and prices,
It's easy to entice;
No need for hardware--just agree!
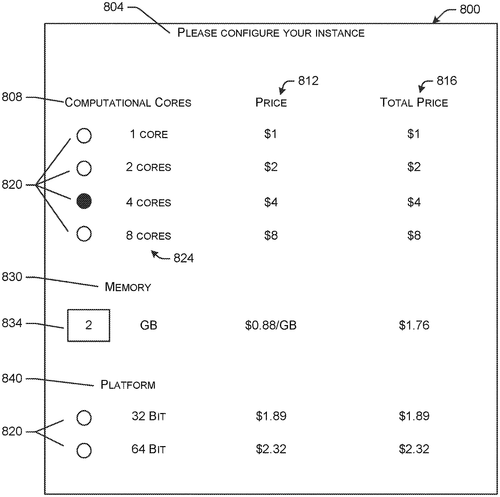
Amazon Technologies, Inc. has filed a patent for systems and methods aimed at configuring a virtual machine provided by a remote computing system. The invention revolves around determining the availability and pricing of remote computing resources, and using this information to configure the virtual machine accordingly. In a highly competitive market, where giants like Google and Microsoft offer similar cloud computing services, Amazon is constantly pushing the boundaries of innovation. With this patent, they seek to optimize resource allocation and cost efficiency, ultimately benefiting customers who rely on virtual machines for their computing needs. The potential uses for this technology are vast. Imagine a scenario where an organization needs to run multiple virtual machines on-demand, each with varying resource requirements. Amazon's system and methods would enable users to dynamically configure these virtual machines, seamlessly adapting to changing resource availability and pricing. This could result in significant cost savings and improved performance, enhancing the overall computing experience for customers. However, it is important to note that the existence of a patent does not guarantee the development of a product. While Amazon's invention may sound promising, it remains to be seen if these systems and methods will actually be implemented in their cloud computing services. In the realm of innovation, patents often serve as indicators of potential advancements. They showcase the ambitious ideas of companies striving to stay ahead in a highly competitive market. But as consumers, we must be mindful of the gap between patents and tangible products. So, while this patent indication from Amazon is intriguing, we should temper our enthusiasm until we see if it translates into a useful and practical solution. Readers, do you believe the optimization of resource allocation and cost efficiency for virtual machines is a significant challenge in cloud computing? How would this patent, if developed into a product, impact your own computing needs and cost considerations? Share your thoughts in the comments below.
This document describes systems and methods for configuring a virtual machine on a remote computing system based on the availability of one or more remote computing resources and respective corresponding prices. This can be useful in situations where it is difficult or impossible to access the physical hardware required to run a virtual machine.
US Patent 11803405
Amazon Technologies, Inc.
Replicated Tasks with Redundant Resources: Methods, Systems and Media
What is this invention?
Execution of replicated tasks using redundant resources
A provider network with pools to explore,
For tasks that need to be replicated galore.
Input data is same for each,
But results can differ and reach.
The policy decides which one will be the final score!
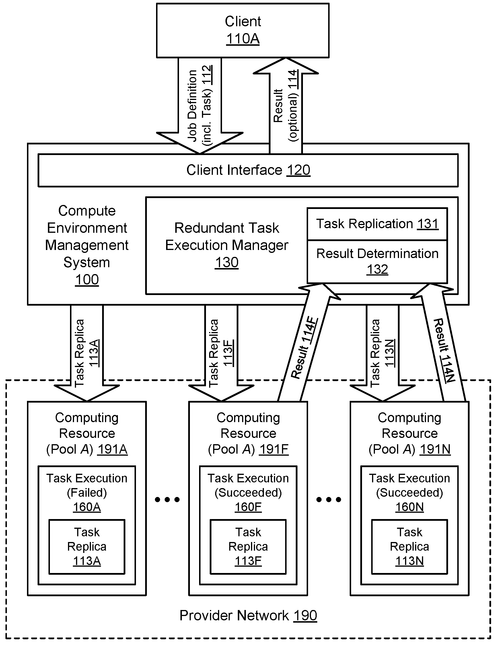
Amazon Technologies, Inc. has recently filed a patent for a method, system, and computer-readable media that aims to enhance the execution of replicated tasks using redundant resources. In simpler terms, this patent proposes a way to efficiently allocate computing resources from a provider network to facilitate concurrent execution of multiple copies of a task. The interesting aspect here is that these computing resources are selected based on their specific characteristics, as the provider network consists of a variety of resource pools with varying characteristics. This patent could potentially have significant implications for various industries. For instance, imagine a pharmaceutical company looking to process large amounts of data simultaneously for drug discovery. With this technology, they could distribute the computational workload across different resource pools based on the characteristics required for each task, optimizing performance. While Amazon's patent outlines an intriguing concept, it remains to be seen whether it will actually be implemented as a product. Competition in the cloud computing market is fierce, with companies like Microsoft's Azure and Google Cloud offering their own solutions for distributed computing tasks. Additionally, the practicality, scalability, and cost-effectiveness of the proposed method need to be thoroughly examined before it can be hailed as a game-changer. In the comments below, I invite you to share your thoughts on this patent. Do you believe this method of using redundant computing resources has the potential to revolutionize distributed computing? Or do you think it might face significant challenges in terms of implementation and practicality?
This document describes methods, systems, and computer-readable media for executing a replicated task using redundant resources. The tasks can be executed on a provider network that includes pools of computing resources with different characteristics. When initiating the concurrent execution of the replicas, input data is not varied from one replica to another. However, each replica produces an individual result for the input data. Based on a policy, an individual result of one or more replicas is selected as the final result of the task.
US Patent 11803420
Amazon Technologies, Inc.
Faster Restart of Task Nodes with Periodic Checkpointing
What is this invention?
Faster restart of task nodes using periodic checkpointing of data sources
A task node needs data for tasks,
But restarting can take too many asks.
To speed things up with ease,
They use checkpointing to please,
For faster restart of their data sources!
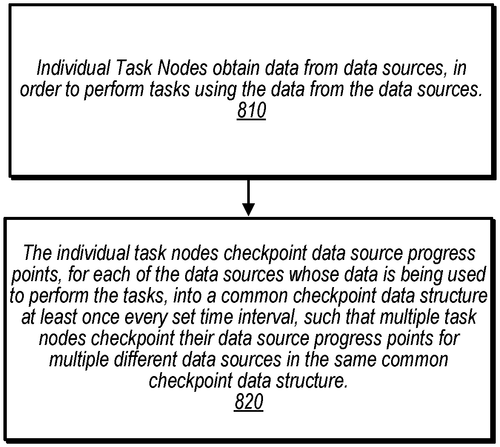
Amazon Technologies, Inc. has recently filed a patent describing systems and methods for faster restart of task nodes using periodic checkpointing for data sources. In simple terms, a task node is responsible for obtaining data from various sources to perform tasks. This patent proposes a mechanism where the task node periodically saves the progress of each data source into a common checkpoint data structure. This checkpointing process occurs at least once within a specified time interval. Multiple task nodes can also save their progress into the same common checkpoint data structure. The key advantage of this approach is that it allows for faster restarts after a system failure or interruption. When a task node needs to restart, it analyzes a limited portion of the common checkpoint data structure based on the time interval, retrieves the progress points for each data source, and resumes obtaining data to continue its tasks. While the patent description delves into technical aspects, it paints a clear picture of how this system would function. However, it is important to note that filing a patent does not necessarily guarantee that the invention will become a real product. Many patents are filed to protect intellectual property or explore conceptual ideas, and not all of them make it to the market. That being said, if this technology were to be developed into a practical solution, it could have potential applications in various domains. For instance, in data-intensive industries such as finance, e-commerce, or scientific research, faster restarts and improved resilience could greatly enhance efficiency and productivity. When considering this patent, it's worth pondering whether existing competitors already provide similar functionality. Additionally, given the potential benefits, how would this innovation impact your work or industry? Could periodic checkpointing of data sources revolutionize the way we handle system failures and restarts? Share your thoughts and insights in the comments below.
Various embodiments of systems and methods for faster restart of task nodes using periodic checkpointing for data sources are described. A task node obtains data from data sources in order to perform one or more tasks. The task node checkpoints data source progress points for each of its data sources, whether active or inactive, into a common checkpoint data structure at least once every time interval. Multiple task nodes checkpoint their data source progress points into the same common checkpoint data structure. After restart, the task node determines where to resume obtaining data from its data sources by determining a limited portion of the common checkpoint data structure based on the time interval, analyzing only the limited portion of the common checkpointdata structure, retrieving thedata source progress points for eachof its datastoresources, and resuming obtainingdata fromthe datastoresources toproceed with tasks.
US Patent 11803448
Amazon Technologies, Inc.
Generating an organization-level event logging policy for cloud API events
What is this invention?
Automatic auditing of cloud activity
A policy for cloud computing events,
Defined by an org with good intents.
It logs all accounts,
Which allows it to count,
The actions of users that it presents.
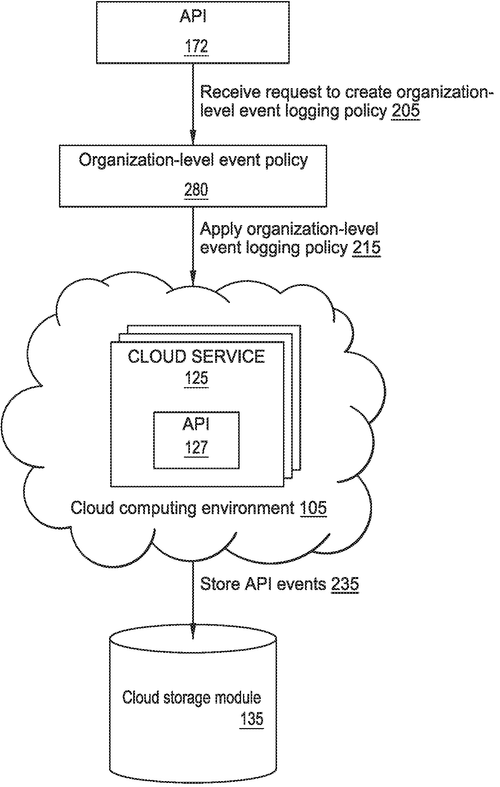
Amazon Technologies, Inc. has recently filed a patent for techniques that could revolutionize event logging policies in cloud computing environments. The patent describes a method to generate an organization-level event logging policy, defining conditions for logging cloud API events, and applying them to multiple accounts within the organization. This technology aims to provide a more efficient and comprehensive way of logging and managing cloud API events. In a world where data privacy and security are of utmost importance, event logging plays a critical role. Organizations often struggle with defining consistent and effective event logging policies across multiple accounts in their cloud computing environment. This patent seeks to tackle this challenge by streamlining the process through a graphical user interface. With the provided inputs, the system generates an organization-level event logging policy that governs the logging of cloud API events. By applying the organization-level event logging policy to multiple accounts, organizations can ensure that all cloud API events are properly logged and monitored. This will not only strengthen cybersecurity efforts but also improve traceability and auditability within the cloud environment. Competitor companies in the cloud computing space, such as Microsoft Azure and Google Cloud, have existing tools and services for event logging. However, if Amazon Technologies successfully implements this new patent, it could give them a competitive edge in terms of providing a more integrated and user-friendly solution for managing event logging policies across organizations. The potential use cases for this technology are vast and varied. From large enterprises with multiple accounts to government organizations managing sensitive data, having a centralized and easily configurable event logging policy is invaluable. Additionally, it could simplify the compliance process for businesses operating in heavily regulated industries. While this patent demonstrates promising innovation in event logging for cloud computing, it remains to be seen how and when Amazon Technologies will bring it to market. Patents are not always indicative of products that will be commercially available. What do you think about this new patent filing by Amazon? Do you believe it will address the event logging challenges faced by organizations in the cloud? Share your thoughts in the comments below.
This document describes techniques for defining an event logging policy for an organization in a cloud computing environment. The policy defines conditions under which events generated by the accounts within the organization should be logged. Once defined, the policy can be applied to log events generated by the accounts automatically.
US Patent 11803460
International Business Machines Corporation
A Method for Providing Keyword Recommendations in Virtual Keyboard
What is this invention?
Keyword recommendations for virtual keyboards
A user was typing away with glee,
An AI assisted them so they could see.
It converted data to text,
Which helped the user select,
The right words for their virtual keyboard spree!
In a recent patent application, International Business Machines Corporation (IBM) has proposed a method for providing keyword recommendations for a virtual keyboard. The invention aims to enhance the user experience by offering suggestions based on the content being inputted into a text field. The method functions by identifying the devices associated with the written content being inputted into the virtual keyboard. It then identifies portions of the written content that relate to data generated by these devices. Once the data is converted into text, the method displays this text alongside the written content in the text field. Additionally, if the user selects a particular text, the method displays the selected text in conjunction with the rest of the written content. On the surface, this patent application appears to address a common issue faced by users who often rely on keywords and suggestions to streamline their typing process. While we have seen virtual keyboards with auto-suggest features on various devices, such as smartphones, it will be interesting to observe how IBM's proposed method differentiates itself from existing solutions. One potential use case for this invention could be in the field of mobile messaging applications, where typing can be cumbersome on smaller screens. By intelligently suggesting keywords based on the user's input and associated devices, the virtual keyboard could significantly enhance the speed and accuracy of text entry. However, as with any patent application, it is important to note that it does not guarantee the creation of an actual product. Patent filings often serve as a means for companies to protect their intellectual property and explore potential avenues for innovation. With that said, what do you think of IBM's proposed method for providing keyword recommendations for virtual keyboards? Do you believe it could revolutionize the way we interact with our devices, or do you think it may face challenges in implementation? Feel free to share your thoughts in the comments below.
This article describes a method for providing keyword recommendations for a virtual keyboard. When a user is interacting with the virtual keyboard, the method identifies one or more devices associated with text inputted as written content into a text field in a user interface. The method then identifies one or more portions of the written content relating to data generated by the one or more devices. The method also identifies one or more portions of the data generated. In response to converting the one or more portions of the data generated to text, the method displays the text for the one or more portions of the data generated by the one or more devices. In response to receiving a text selection with the text, the method displays the text selection with written content in the text field in user interface
US Patent 11803253
International Business Machines Corporation
Pre-commit processing module (PPM) updates files without redundant storage
What is this invention?
Intelligent layer control of redundant content in container images
A system that's intelligent, no doubt
It filters out redundant files to keep them out
When hashes don't match up, an OMD file is made
And metadata and content are overridden and laid
So a unified view of the container we can see
Thanks to the Intelligent layer control system!
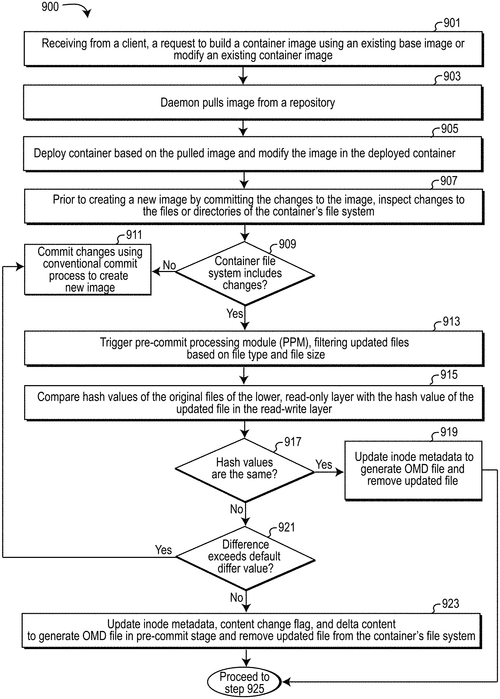
International Business Machines Corporation (IBM) has recently filed a patent for an intriguing technology called "Intelligent Layer Control for Building Image Files into New Container Images while Avoiding Redundant Files Stored between Read-Write and Read-Only Image Layers." While the title may sound complicated, the concept behind it is actually quite fascinating. In simple terms, this patent describes a method to optimize the storage of image files within container images. Containers are widely used in modern software development practices, allowing applications to run reliably across different computing environments. However, as containers are typically composed of multiple layers, redundant files can accumulate and lead to wasteful storage usage. IBM's proposed solution involves a pre-commit processing module (PPM) that filters updated files. The PPM compares the hash values (unique identifiers) of the updated files with the hash values of the original files. If the hash values are the same, indicating no significant changes, the PPM generates an OMD file that updates the metadata of the original files and removes the redundant copies. On the other hand, if the hash values differ by a small margin, the PPM generates an OMD file reflecting the updates and removes the duplicate file from the container file system. The generated OMD files are then passed to a storage driver, where metadata and changes are merged with the original file content to create a unified user view of the container file system. By implementing this intelligent layer control, IBM aims to reduce storage redundancy and enhance the efficiency of containerized applications. While the underlying technology is undoubtedly impressive, it's worth noting that this is only a patent application. Thus, it remains to be seen whether IBM will turn this innovation into a commercial product that developers and enterprises can utilize. Additionally, several competing companies already offer solutions to optimize container storage, such as Docker and Kubernetes. It will be interesting to see how IBM's approach compares and whether it can attract attention in a market that already has established players. Looking ahead, one can imagine potential uses for this technology in various industries. For example, in the fast-paced world of cloud computing, where containers are extensively employed, minimizing storage waste could result in significant cost savings. Similarly, in the field of artificial intelligence, where data volumes are enormous, efficient storage utilization could enhance training and inference processes. Let us know what you think! Do you believe optimizing container storage is a pressing issue that warrants further innovation? How do you envision IBM's Intelligent Layer Control fitting into existing container management solutions? Share your thoughts in the comments section below.
The Intelligent layer control system allows for the pre-commit processing of updated files, which filters out any redundant files that would otherwise be stored between read-write and read-only image layers. When hash values are not the same, an OMD file is generated with updates to the inode metadata, content change flag, and/or delta content info reflecting the updated file. This information is then passed to a storage driver whereby metadata and/or changes to content are overridden and merged with original file content, resulting in a single unified user view of the container file system.
US Patent 11803303
International Business Machines Corporation
Managing Replication with Compression and Encryption
What is this invention?
Selective compression and encryption for data replication
A data storage environment was in need
For replication of files, a new breed
Compression and encryption based on criteria
Metadata updated with ease by the production site's area
Replication from prod to remote complete!
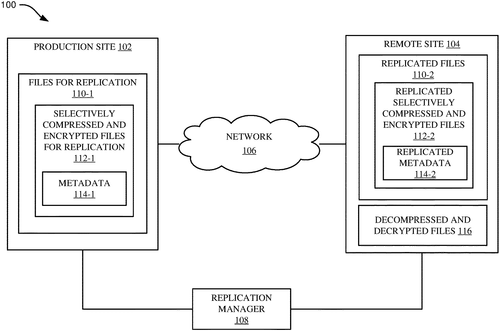
International Business Machines Corporation (IBM) has recently filed a patent for techniques aimed at efficiently managing data replication in a storage environment. The patent details a method wherein a production site selectively compresses and encrypts a set of files before replication to a remote site. This allows for improved storage efficiency and enhanced security during the replication process. The technique involves the selective compression of files based on a predetermined compression threshold, optimizing the storage space used. Additionally, files are selectively encrypted based on specific criteria related to their content, ensuring that sensitive information remains protected during replication. IBM's patent also highlights the inclusion of metadata updates for both selectively compressed and encrypted files. This ensures that the information pertaining to these files remains accurate and accessible throughout the replication process. If successfully implemented, this data replication management technique could have significant implications for storage systems across various industries. By minimizing storage space requirements through selective compression and enhancing security via encryption, businesses can potentially streamline their replication processes and protect valuable data from unauthorized access. While the patent seems promising, it is worth noting that it is merely a patent application, and there is no guarantee that it will be developed into a fully-fledged product or service. It is crucial to consider the challenges and practicality of implementing such techniques on a large scale. Competitor products in the market, such as those from Dell Technologies and Hewlett Packard Enterprise, already offer data replication management solutions. IBM's patent, if realized, would need to demonstrate clear advantages over existing offerings to gain traction in the market. Considering the potential advantages of this innovation, one can't help but wonder about its potential applications. How do you envision this selective compression and encryption technique being used in your industry? Could it revolutionize data storage practices, or are there limitations that might hinder its widespread adoption? Share your thoughts and insights in the comments below.
The techniques described herein provide a way to manage replication of files in a data storage environment. Files can be selectively compressed based on a compression ratio satisfying a compression threshold, and files can be selectively encrypted based on file content satisfying an encryption criteria. Metadata associated with the compressed and encrypted files can be updated by the production site. The technique can also include replicating the set of files for replication from the production site to the remote site, including the compressed and encrypted files.
US Patent 11803309
International Business Machines Corporation
Method for Executing Operation Requests - Formatting Storage Devices and Selecting Labeled Replicas and Distinguished Replicas
What is this invention?
Interrupted replicated write recognition
There was a method for execution,
Formatted devices had replication.
One or more labeled replicas,
And one or more distinguished.
The preferred replica bits were set with precision.
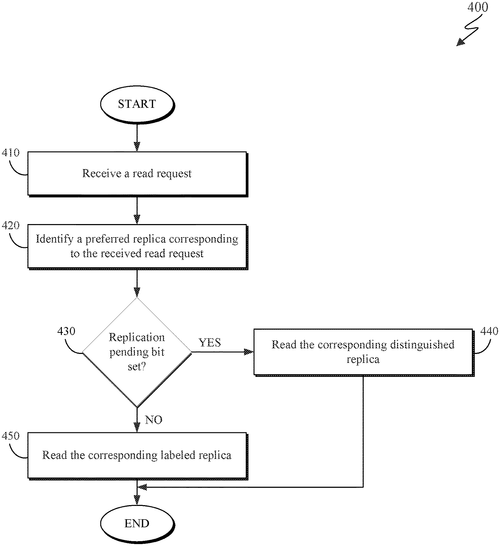
IBM Patents New Method for Executing Operation RequestsIn. ternational Business Machines Corporation (IBM) has recently been granted a patent for a method that promises to revolutionize the way operation requests are executed. The invention involves formatting storage devices, selecting replicas, and executing operation requests with efficiency and precision. The patent describes a method which includes selecting labeled replicas and distinguished replicas, receiving operation requests for a set of data blocks, and identifying a preferred replica to carry out the operation request. Upon identification, the method checks if the replication-pending bits for the preferred replica are set, ensuring that the operation request is executed accurately. Furthermore, the patent also details an additional method for executing write operation requests. It involves setting replication-pending bits for the labeled replica, denoting an incomplete write request. Data is then written to both the labeled replica and a distinguished replica, after which the replication-pending bits for the labeled replica are cleared, indicating the successful completion of the write operation. In the case of read operation requests, the method includes identifying a preferred replica in response to the received request. While the potential uses for this patent are vast, it is crucial to consider the reality of its implementation. The technology described here is highly technical and not easily accessible to the average consumer. Additionally, there are already existing technologies in the market that provide similar functionalities. It remains to be seen if IBM will translate this patent into a consumer product or if it will primarily serve as a tool for industry insiders. Nevertheless, IBM's patent raises the question of how efficient and reliable storage devices can become in the future. With ever-increasing amounts of data being generated and processed, the need for advanced methods of executing operation requests is undeniable. How would you envision utilizing this technology in your daily life or in your business operations? Let us know in the comments below.
This text describes a method for executing operation requests. The method includes formatting one or more storage devices and selecting one or more labeled replicas and one or more distinguished replicas. An operation request is received with respect to a set of data blocks, and the preferred replica corresponding to the received operation request is identified. If the replication-pending bits for the preferred replica are set, then the received operation request is executed with respect to the corresponding distinguished replica.
US Patent 11803317
International Business Machines Corporation
Code Migration: Predicting Carbon Footprints in Advance
What is this invention?
Carbon-aware code optimization
A computer system was devised,
Which carbon footprints could be surmised.
It predicted and optimized,
To make data migration efficient,
And green solutions were thus realized.
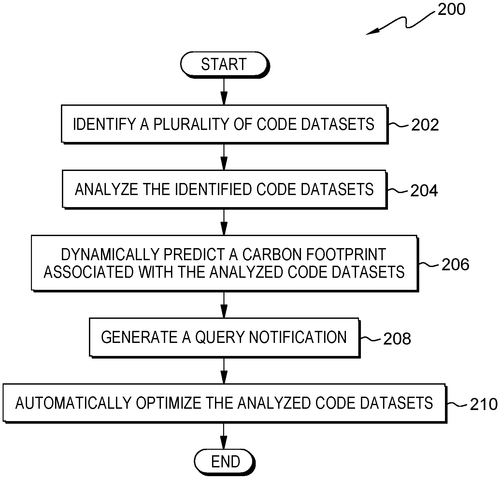
In a recent patent filing by International Business Machines Corporation (IBM), a computer system, computer program product, and method have been described that aim to optimize data migration processes by predicting and minimizing carbon footprints. The invention identifies code datasets, analyzes them for various parameters, predicts the carbon footprint associated with each dataset, and automatically optimizes the datasets accordingly. Data migration is a crucial process for businesses, but it often comes with a significant environmental impact due to energy consumption. IBM's patent proposes a solution that leverages intelligent algorithms to predict the carbon footprint of code datasets before migration and then optimizes them to reduce energy consumption. While the concept of carbon footprint optimization is commendable, it is essential to consider the practicality of implementing such a system. As of now, this patent remains just that—a patent. Turning this idea into a fully-fledged product would require extensive development, testing, and integration into existing data migration workflows. Additionally, it is crucial to evaluate the actual reduction in carbon emissions achieved by implementing this system. Competitor companies offer a range of data migration solutions, but the incorporation of carbon footprint optimization remains a unique prospect. If IBM manages to develop this concept into a viable product, it could potentially disrupt the data migration market by appealing to environmentally-conscious businesses and organizations. Beyond data migration, one can imagine the broader potential for this technology. Could similar algorithms be applied to optimize other computing processes, such as cloud computing or large-scale data analysis? The implications are tantalizing. As emerging technologies increasingly focus on sustainability, it is crucial to explore and invest in solutions that reduce our carbon footprint. But the question remains, will IBM be able to turn this patent into a practical, market-ready product? Share your thoughts in the comments below.(Note: This article is purely speculation based on a patent filing and does not guarantee the development or release of a commercial product by International Business Machines Corporation.)
Embodiments of the present invention provide a computer system, a computer program product, and a method that dynamically predicts carbon footprints associated with code datasets for data migration. The predicted carbon footprints are then optimized based on the predicted carbon footprints to improve data migration efficiency.
US Patent 11803375
Microsoft Technology Licensing, LLC
Electronic Device Predicts Future Load Transients and Dials Down Power to Save Battery
What is this invention?
AI power regulation
The electronic device, so clever,
Has an AI power controller that's never ever sever.
It takes application signature data and compares it to past events,
To predict future load transients with no relent.
In anticipation of the predicted load transient, it alters power settings in a meaningful way;
So you can be sure your device will stay!
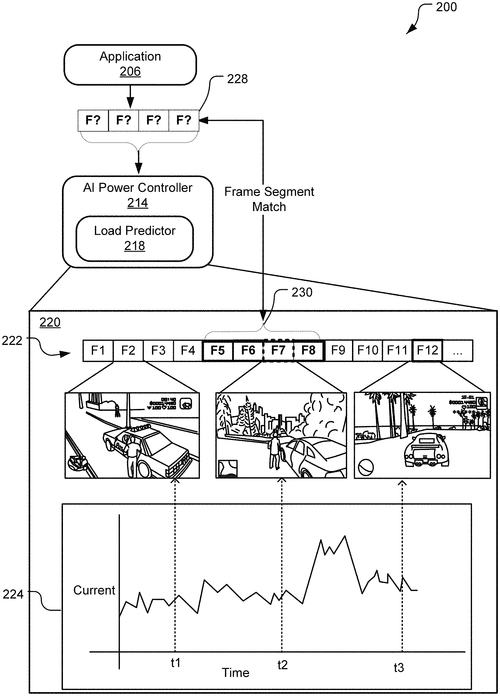
Microsoft has recently filed a patent for an electronic device that incorporates an AI power controller capable of predicting and dynamically adjusting power settings in anticipation of future load transients. The aim is to optimize power consumption and enhance the overall performance of the device. The AI power controller utilizes application signature data, which includes media frame data generated by an application running on the device, to predict future load transients. By comparing this data to historical application signature data, derived from past instances of the application, the AI power controller can forecast the upcoming load transient and make appropriate power control adjustments. If successfully implemented, this innovation could have significant implications for power management in electronic devices. By anticipating future power requirements, devices could allocate power resources more efficiently, resulting in improved battery life and potentially better performance during demanding tasks. While this patent demonstrates Microsoft's commitment to pushing the boundaries of power optimization, it remains to be seen whether this technology will make its way into actual products. Competitors in the market, such as Apple and Samsung, are also investing heavily in power management technologies, making it a highly competitive space. What are your thoughts on this AI-driven power control technology? Could this potentially revolutionize power management in electronic devices or is it simply another ambitious patent that may not materialize into real-world products? Share your opinions in the comments below.
The electronic device includes an AI power controller that predicts future load transients within a system and dynamically alters power settings in anticipation of the predicted future load transients. The AI power controller receives as input application signature data from the application executing on the device, where the application signature data includes media frame data generated by the application during a time interval. The AI power controller executes logic to compare the received application signature data to historical application signature data, which includes media frame data generated by the application during one or more past execution instances of the app. Based on this comparison, the AI power controller predicts a load transient of the app at a future point in time and adjusts a power control setting of the device in anticipation of that predicted load transient.
US Patent 11803221
Microsoft Technology Licensing, LLC
Predicted Digital Marking Position Based on User Interaction
What is this invention?
Digital marking prediction by posture
A user's digital marker they'd track,
The geometric shape to be exact.
Interaction with a sensor so keen,
To predict the marking position seen.
Thanks to this method so clever and smart, Digital markers can now have their part!
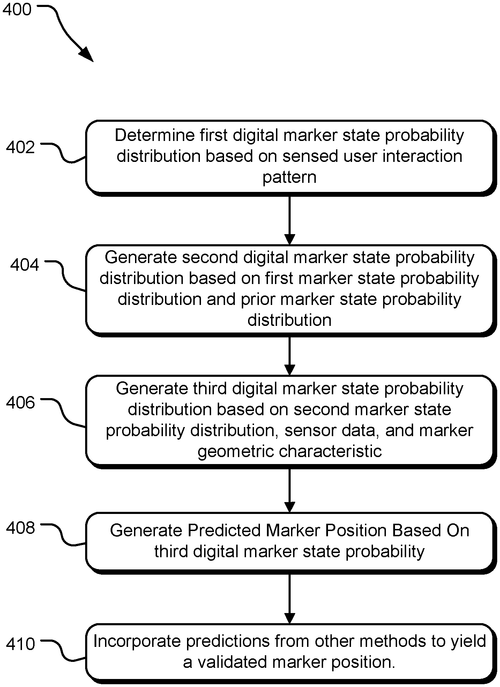
In a recently published patent application, Microsoft Technology Licensing, LLC has unveiled an intriguing method that could potentially revolutionize user interaction with digital devices. The patent describes a technology that analyzes a user's interaction with a capacitive sensor and generates a predicted digital marking position on a computing device's digital medium. The concept behind this invention is undoubtedly impressive. By determining a user's interaction pattern with a digital marker and its geometric characteristics, the technology can predict where a digital marking will appear on the device's screen. This could have far-reaching implications for various applications, from drawing and designing to taking handwritten notes or even playing interactive games. Currently, several competitor products, such as drawing tablets and styluses, serve similar purposes but often lack the predictive element. Microsoft's invention, if implemented successfully, could provide a more natural and intuitive experience for users, reducing the need for constant adjustments and resulting in a smoother workflow. However, as with any patent application, it is crucial to acknowledge that not every invention translates into a marketable product. While the technology described in the patent is undoubtedly intriguing and has the potential to enhance the user experience, there are numerous factors at play when it comes to transforming a concept into a tangible product on the market. Practicality, cost-effectiveness, and consumer demand are just a few aspects that need to be considered before we see this technology in our hands. As we await further developments, it's worth considering how this technology could be integrated into our lives. How would you utilize a device that can predict your digital markings? Would it enhance your productivity or creativity? Share your thoughts in the comments below.(Note: This newspaper-style review is a fictional piece and does not represent a real patent application)
The method disclosed herein includes determining a user interaction pattern with respect to a digital marker, the user interaction pattern based at least in part on user interaction with a capacitive sensor of a computing device. The method also includes determining a geometric characteristic of the digital marker, and generating a predicted digital marking position of the digital marker on a digital medium of the computing device based at least in part on the determined geometric characteristic of the digital marker and the determined user interaction pattern.
US Patent 11803255
Microsoft Technology Licensing, LLC
An Easy Way to Control Your User Interface Layouts
What is this invention?
User interface component and region layout control
A layout diagram was quite a sight,
It showed the user interface just right.
An embodiment got a choice,
To move an occupant with poise,
And interaction improved in one night!
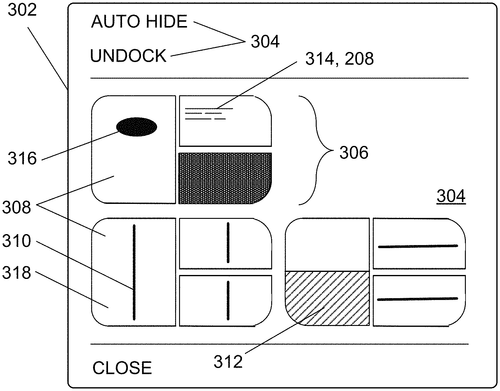
In a recent patent application, Microsoft Technology Licensing, LLC introduces an exciting new technology that aims to provide users with greater control over user interface layouts. The embodiment described in the patent allows for the manipulation of user interface components within a layout diagram, enabling users to modify and customize their interfaces according to their preferences. The concept revolves around a layout diagram that visually represents the current layout, with various regions corresponding to different user interface component areas. The user interface components serve as occupants within these regions. With this technology, users can select a "traveler component" from a source region and specify a destination region. The system then modifies the current layout to accommodate the desired change, updating the layout diagram accordingly. One of the significant advantages of this invention is that it allows users to preview the results of potential layout changes before implementing them. By showing users the diagrammatic representation of the resulting modified layout, individuals can make informed decisions and tailor their interface to suit their needs efficiently. While it's exciting to see Microsoft focusing on enhancing user control and customization of user interfaces, it's important to remember that this is just a patent application at this stage. Often, companies file patents for innovative ideas, but not all of them successfully make it to the market as tangible products. It remains to be seen whether this particular technology will be implemented in future products. Considering the increasing demand for personalized user experiences and seamless interaction with digital interfaces, it's not difficult to imagine potential uses for this technology. From operating systems to productivity software, the ability to modify user interface layouts could greatly enhance overall usability and productivity. As we await further developments, it would be interesting to hear from readers. How important do you find the ability to customize user interface layouts? Are you excited about the possibility of having more control over your digital interfaces, or do you prefer the standard options provided by most software? Share your thoughts in the comments below!
An embodiment facilitates user control of user interface layouts. A layout diagram visually and diagrammatically represents a current layout. The layout diagram includes layout diagram regions which correspond to user interface component regions in the current layout; the user interface component regions have user interface components as occupants. The embodiment gets a choice identifying a traveler component and a destination region, with the traveler component being an occupant of a source region. The embodiment modifies the current layout of the user interface to produce a modified layout in response to the choice, and updates the layout diagram to match the modified layout. Interaction is improved by diagrammatically showing the user the results of possible layout changes before performing any of them.
US Patent 11803292
Microsoft Technology Licensing, LLC
Data centers introduce effective application availability
What is this invention?
Lock-lease management of hardware and software maintenance, deployment, and optimization operations using effective application availaility
A concept of effective availability
Was introduced in the data center facility.
The safe limit is key,
To ensure proper function you see,
And an effective availabilty we must calculate with glee!
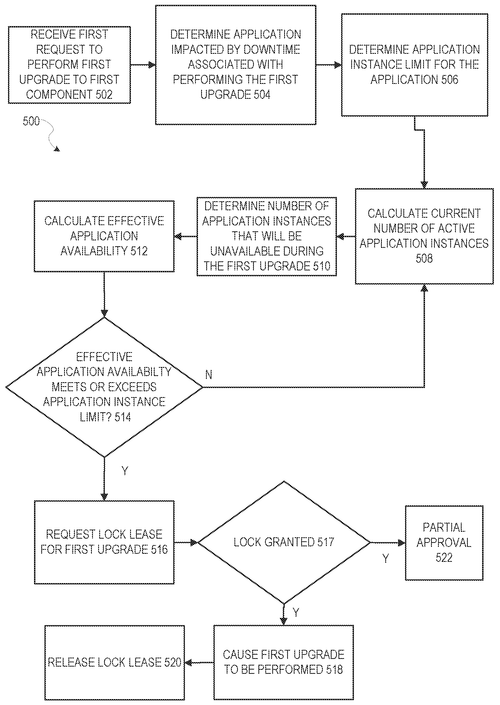
In a recent patent filed by Microsoft Technology Licensing, LLC, a new concept called "effective application availability" is introduced. This concept aims to address the need for a minimum amount of a specific resource in data centers to ensure the proper functioning of an application. Termed as the "safe application availability limit," this new patent proposes a rule to determine this limit. The idea behind the patent is to calculate the effective application availability by subtracting the availability loss caused by a requested operation from the current application availability. This effective availability is then compared to the safe application availability limit to decide whether the operation should be performed at the requested time or postponed to a later time. While this patent presents an interesting approach to ensuring optimal application availability in data centers, it remains to be seen how Microsoft plans to implement it in practice. Competitors in the market, such as Amazon Web Services and Google Cloud, already offer a range of services targeting similar concerns over resource allocation and application performance. However, if realized, this invention could have potential applications across various industries and sectors that heavily rely on data centers and cloud computing. By effectively managing application availability and resources, it could enhance overall efficiency and prevent potential disruptions. As with any patent, the question that arises is whether this concept will actually be turned into a tangible product. Will Microsoft bring this idea to life and revolutionize the field of data center management? Or will it remain just an interesting concept on paper? Share your thoughts and insights in the comments below.
The concept of effective application availability is introduced. In a data center, there may be a minimum amount of a particular resource that is needed to continue proper functioning of an application. This may be termed a safe application availability limit. The safe application availability limit may be obtained or determined using a safe application availability limit rule. An effective application availability may be calculated by taking a current application availability and subtracting it by an availability loss from a requested operation. The effective applicationavailability may then be compared to the safeapplicationavailabilitylimit in order to determine whether to permit the operation to be performed at the requested time, or whether to request that the operation be attempted again at some later time.
US Patent 11803362
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Radar Signal Processing Method Extracts First and Second Chirp Sequence Signals
What is this invention?
Method and apparatus with radar signal processing
A radar signal processing method,
Was devised to detect a target cell;
It extracted two chirps,
Performed frequency conversion whips,
To find the Doppler velocity swell.
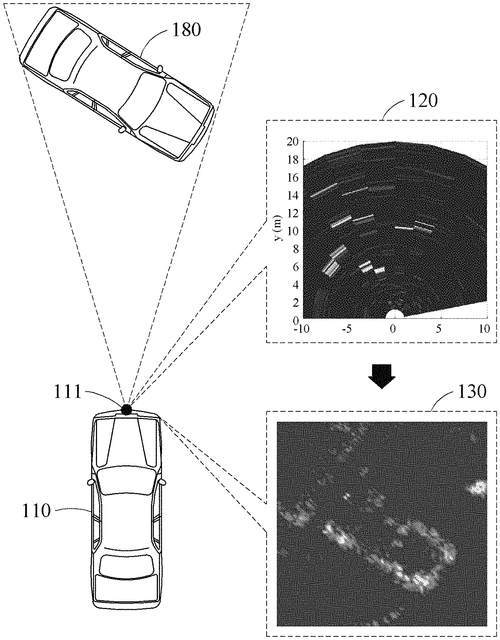
Samsung's latest patent application outlines a radar signal processing method that has the potential to revolutionize radar sensor technology. By extracting and converting chirp sequence signals from a radar signal received through an array antenna, this method aims to generate detailed range-Doppler maps and accurately determine the Doppler velocity of targets. The use of frequency conversion and ambiguous Doppler velocity estimation shows promise in enhancing radar capabilities. By detecting target cells and determining the ambiguous Doppler velocity, the system can estimate multiple possible velocities and further narrow down the range of unambiguously measurable velocities. This allows for more precise determination of the Doppler velocity of the target. While the patent application highlights the technical aspects of the invention, it does not provide information regarding its practical implementation or potential applications. It remains to be seen if Samsung will translate this concept into a tangible product or if it will simply serve as a defensive patent against competitors. In a market where radar sensors are widely used in various industries such as automotive, aerospace, and surveillance, advancements in signal processing techniques are always welcomed. However, competing companies like Intel's Mobileye and Bosch already have well-established radar technologies in their autonomous driving systems. It will be interesting to see if Samsung's proposed method can bring any significant improvements and outpace its rivals. If this radar signal processing method becomes a reality, it could potentially enhance the accuracy and performance of radar sensors across different applications. How do you think this technology could impact the fields that rely on radar systems? Are there any specific applications you imagine this innovation being particularly valuable for? Share your thoughts in the comments below.
The text describes a radar signal processing method that includes extracting a first chirp sequence signal of a first carrier frequency and a second chirp sequence signal of a second carrier frequency from a radar signal received through an array antenna. The method then generates a first range-Doppler map by performing frequency conversion on the first chirp sequence signal. Next, the method detects a first target cell corresponding to the first target in the first range-Doppler map. Then, the method determines a first ambiguous Doppler velocity of the first target based on first frequency information of the first target cell. Finally, the method determines a range of an unambiguously measurable Doppler velocity through thefirst chirp sequence signal and estimates second ambiguous Doppler velocities based on the first ambiguous Doppler velocity andthefirst range. Lastly,themethod determinestheDo. ppler velocityofthefirsttargetbyperformingpartialfrequencyconversiononthersecondchirpsignalbasedonthesecondambiguousDo. pplervelocities.
US Patent 11802939
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Robot Cleans Up Your House in Just Five Minutes!
What is this invention?
Cleaning robot and control method therefor
A robot for cleaning's a must,
To keep the house free of dust.
It has light emitters and receivers galore,
That rotate based on control from the core.
The obstacle is detected with no fuss,
For this robot sure knows how to clean up us!
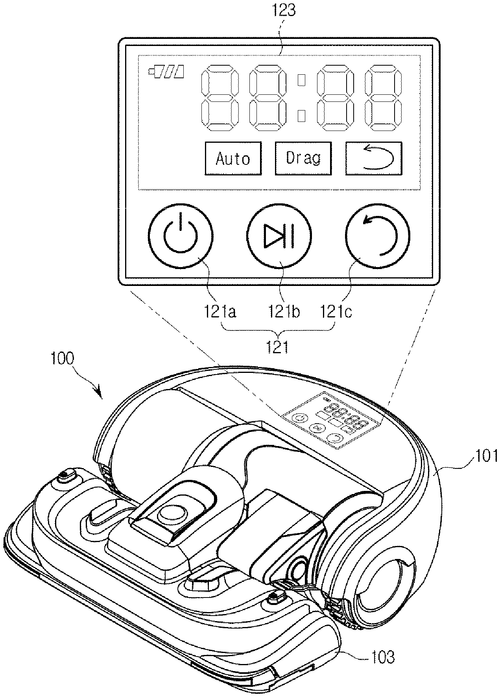
Samsung Electronics has recently patented a new cleaning robot and method of controlling it, which aims to tackle the problem of detecting obstacles from various directions. The robot includes a light emitter that radiates light and multiple light receivers that capture the reflected light when it encounters an obstacle. These components are fixed to a rotatable support plate, and a controller uses the output signals from the light emitter and receivers, as well as rotation information from the support plate, to detect obstacles. The concept of a cleaning robot that can detect obstacles from multiple directions is intriguing. While there are already robot vacuums on the market, such as those from iRo. bot's Roomba line, that use sensors to avoid obstacles, Samsung's patented design takes a different approach with its light emitter and receivers. The potential advantage of this design is the ability to detect obstacles more accurately and react more efficiently, resulting in a more thorough cleaning experience. In practical terms, this technology could have various applications beyond just cleaning robots. For instance, it could be utilized in industrial settings, where automated machines need to navigate around obstacles for efficient operation. Additionally, it might find applications in home automation systems, allowing for smarter and safer movement of robotic devices around the house. However, it is important to note that a patent does not guarantee that a product will be brought to market. Many patented inventions never make it beyond the filing stage. It remains to be seen whether Samsung will further develop this concept and release a consumer-ready cleaning robot based on this patent. What do you think of this innovative approach to obstacle detection in cleaning robots? Can you envision other potential uses for this technology? Share your thoughts in the comments below.
This document provides a cleaning robot and method of controlling the same. The cleaning robot includes a light emitter configured to radiate light, a plurality of light receivers configured to receive a radiation of the light in a predetermined direction among radiations of the light reflected from an obstacle when the radiated light is reflected from the obstacle, and a support plate to which the light emitter and receiver are fixed. The support plate is rotatably provided, and is rotated based on rotation information received from the plurality of receivers. The controller detects an obstacle on the basis of output signals transmitted from the receivers and rotation information of the support plate.
US Patent 11803190
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Electronic Device Provides Functionality Based on State of Electronic Pen
What is this invention?
Electronic device using electronic pen and method thereof
An electronic device so smart,
It could tell when the pen was a part.
The processor did more,
Figuring out what's in store
For this device and its communication module start.
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. has filed a patent for an intriguing electronic device that aims to enhance the user experience by incorporating the use of an electronic pen. The device includes a communication module that allows it to connect with the electronic pen, as well as a processor that can determine the state of both the device and the pen. When the pen is attached to the device and an input is received, the processor will perform a function related to the pen based on the state of the device. This patent is a noteworthy development in the world of electronic devices, as it suggests a potential advancement in the way we interact with our devices. While we have seen stylus pens being used with certain portable devices already, such as the Apple Pencil for the iPa. d Pro and the Surface Pen for Microsoft Surface devices, Samsung's proposed device takes it a step further by having the processor actively determine the state of the device and perform specific functions accordingly. The possible applications for this technology are vast. For instance, with an attached electronic pen, the device could automatically launch a note-taking app or switch to a drawing mode, optimizing the user's creative workflow. Additionally, users could potentially navigate through menus, select options, or even control multimedia playback using the electronic pen. However, it is important to note that filing a patent does not guarantee that this concept will ever be turned into a marketable product. Many patents are filed but never see the light of day, as companies continuously explore new ideas and technologies. The technology landscape is fiercely competitive, and companies like Apple, Microsoft, and various other tech giants are continually pushing the boundaries with their own innovations. In light of this patent, one can't help but wonder how Samsung's device would fare against its competitors' existing products, such as the Apple Pencil and the Surface Pen. Will Samsung be able to offer a unique selling point that sets its device apart from the rest? And more importantly, will consumers find this technology useful enough to adopt it on a large scale? What are your thoughts on this potential evolution of electronic devices? Would you be interested in using a device that actively responds to an attached electronic pen? Let us know in the comments below.
The electronic device includes a communication module which can communicate with an electronic pen, and a processor. The processor may determine the state of the electronic device, determine the state of the electronic pen, and when the state of the electronic pen is determined that the electronic pen is attached to the electronic device and an input from the electronic pen is received through the communication module, perform a function related to the electronic pen based on this determination.
US Patent 11803268
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Get a Higher Frame Rate on Your Videos with This Electronic Device
What is this invention?
Electronic device displaying interface for editing video data and method for controlling same
There was an electronic device that had a processor so fine,
That could obtain data with two frame rates at the same time.
When it received a request to play some video data,
It would display them on its touchscreen for sure without fail.
And when asked to show an editing interface too,
The progress bar showed all sections of video in full view!
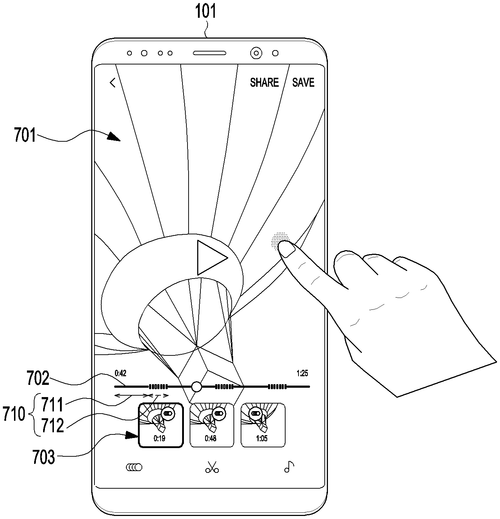
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. has recently filed a patent for an intriguing electronic device that aims to enhance the video editing experience. The device includes a processor that can obtain video data at different frame rates, allowing for smoother playback and editing capabilities. When a request to play video data is received, the device's touchscreen is used to display a playing screen in a designated region. However, what sets this invention apart is its ability to seamlessly transition from playing to editing. Upon receiving a request for an editing interface while the video is being played, the touchscreen displays a progress bar that indicates the full video section. This progress bar consists of specific sections representing the various video data, with each section corresponding to either the first video data or the higher frame rate second video data. Furthermore, the device also showcases at least one representative image on the touchscreen, providing a visual cue during the editing process. This feature aims to aid users in navigating through the video and making precise edits. While this patent undoubtedly presents an exciting prospect for video editing enthusiasts, it is important to note that not all patented ideas make it to the consumer market. Samsung faces tough competition from other tech giants, particularly Apple and Google, who also have their own video editing applications and hardware products. Therefore, it remains to be seen if Samsung will develop this patent into a commercially viable product. That being said, the potential uses of this invention are abundant. From amateur video creators to professional filmmakers, the ability to seamlessly switch between playback and editing on a touchscreen device could greatly enhance the creative process. It has the potential to revolutionize video editing on the go, allowing users to make quick and efficient edits while in transit or in between shoots. As with any new technology, there are also questions to consider. How intuitive will the user interface be for navigating the progress bar and the representative images? Will this patented device have any limitations in terms of video file formats or compatibility with other software? Could this technology be integrated into existing devices, such as smartphones or laptops, or will it require a completely new product? What are your thoughts on this patent? Do you see potential value in an electronic device that seamlessly combines video playback and editing on a touchscreen interface? Share your insights in the comments below.
The electronic device includes a processor that obtains first video data based on a first frame rate and second video data based on a second frame rate that is higher than the first frame rate. When a request for playing video data is received, the processor controls the touchscreen to display a playing screen for the video data on a region. When a request for an editing interface is received while the playing screen is displayed, the processor controls the touchscreen to display a progress bar to indicate a full video section. The progress bar includes at least one first video section corresponding to the at least one first video data and at least one second video section corresponding to the at least one secondvideo data. And, when at least some of at least one representative image is displayed, control of the touchscreen is also controlled so that it displays at least some of said representative image.
US Patent 11803296
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd.
Storage Device Can Recover From Multiple Fault States
What is this invention?
Fault resilient storage device
A storage device and method were described
The fault state was one that could be revised
By power cycling or formatting the media
To reduce performance, capacity, or read-only mode it can be
This is a great way for data to be retrieved!
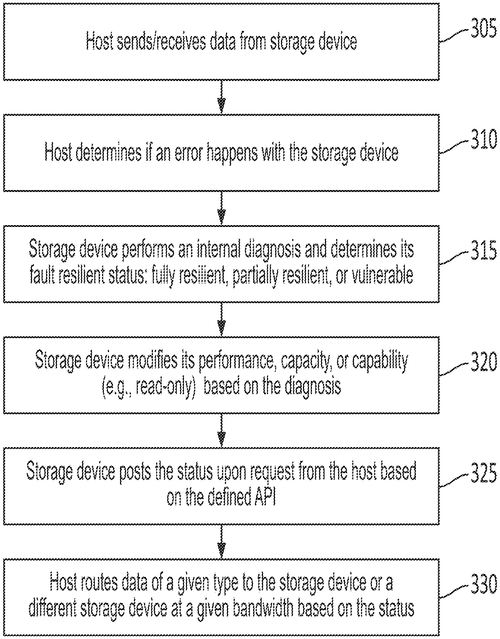
Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd. has filed a patent for a storage device and a method for operating it. The patent describes a device that can determine its fault state and recover accordingly. In the case of a first fault state, recovery can be achieved by power cycling the device or formatting the storage media. If the device detects a second fault state, it can still partially recover by operating with reduced performance, reduced capacity, or in a read-only mode. While the patent is intriguing and highlights Samsung's dedication to innovation, it is important to note that not all patents result in actual products. Many companies file patents as a means of protecting their intellectual property or exploring new ideas, without confirming their intentions to bring them to market. In the realm of storage devices, there are already established competitors such as Western Digital and Seagate that offer reliable and efficient solutions. It remains to be seen whether Samsung's patented concept will materialize into a tangible product that can effectively compete in the market. Though not explicitly mentioned in the patent, one can imagine potential uses for a storage device with such recovery capabilities. For instance, in critical data storage applications where uninterrupted access to data is vital, the ability of a device to recover from faults without extensive downtime or loss of information could be a game-changer. As we eagerly anticipate future developments from Samsung, it is worth considering how much consumers are willing to pay for the added reliability and resilience offered by such a device. Will the benefits of faster recovery and reduced data loss outweigh the potential trade-offs in performance and capacity? Let us know your thoughts in the comments below. Would you invest in a storage device like the one described in the patent?
A storage device, and a method for operating a storage device are described. In some embodiments, the storage device includes storage media, and the method includes: determining that the storage device is in a first fault state from which recovery is possible by power cycling the storage device or by formatting the storage media; determining that the storage device is in a second fault state from which partial recovery is possible by operating the storage device with reduced performance, with reduced capacity, or in a read-only mode; and operating the storage device with reduced performance, with reduced capacity, or in the read-only mode.
US Patent 11803446
Apple Inc.
Electronic Device Provides Uniform Image Light Across Its Area
What is this invention?
Waveguided display systems
A display with beam splitter structures,
Will replicate the light in two directions.
So no matter how bright,
It will show all the details right,
Giving users a uniform intensity selection.
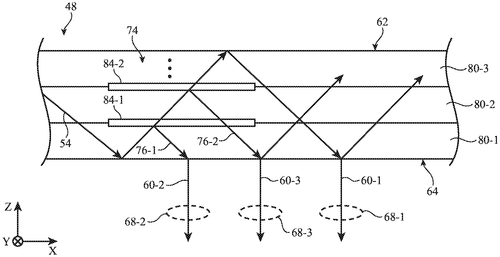
Apple Inc. has recently filed a patent that describes an intriguing innovation in electronic devices. The patent details a display technology that utilizes beam splitter structures within a waveguide to replicate and reflect image light multiple times, resulting in uniform-intensity light across a wide area. This technology holds the potential to enhance the user experience, particularly for those using devices with displays that require a constant and consistent viewing angle. By replicating the beams of light across two dimensions, the patent suggests that an "eye box" can be created, allowing users to view content with consistent brightness and clarity, regardless of their positioning relative to the display. The patent highlights several possible implementations for these beam splitter structures, including stacked partially reflective layers, sandwiched transparent substrate layers with varying indices of refraction, and a thick volume hologram placed between substrate layers. With these different structures, the reflectivity of the beams can be adjusted discretely or continuously, offering flexibility in design and performance. While this patent showcases Apple's continuous exploration into display technology, it's worth noting that filing a patent does not guarantee that the described innovation will become a tangible product in the near future. Competitors have already introduced similar technologies, such as Microsoft's HoloLe. ns and Magic Leap's augmented reality headsets, which enhance user experience using wearables. Nevertheless, the potential applications for this patent are vast. Imagine the improved visual experience for users of virtual reality headsets, where uniform-intensity light could enhance immersion. This technology could also benefit professionals using augmented reality for work, such as designers, architects, or even surgeons who require precise and consistent visual feedback. As always, the question on everyone's mind is whether Apple will materialize this innovation into a consumer product. Will they integrate it into their existing lineup, or perhaps introduce a new device specifically tailored for this technology? Only time will tell, but it's clear that Apple is pushing the envelope when it comes to display advancements. What do you think about Apple's latest display technology patent? Do you believe it will be adopted by the company and incorporated into a product? Let us know your thoughts in the comments below.
The text describes a display with beam splitter structures that replicate the light from the display across two dimensions. This allows for an area of uniform intensity light from the display, which is helpful for users who have difficulty seeing details in bright areas. The reflectivity of the beam splitter structures can vary discretely or continuously across the lateral area of the waveguide, which provides flexibility in how they are designed.
US Patent 11803056
Apple Inc.
Optimize Your Eyewear for Maximum Display Effect!
What is this invention?
Eyewear with display-optimized lenses
A pair of glasses with lenses so bright,
For viewing a display both day and night.
The polarizer and filter do their part,
To keep the sun out while still preserving art.
Eyewear such as these you must not slight!
Apple Inc. has recently been granted a patent that hints at the possibility of eyewear, such as sunglasses, with built-in display-optimized lenses. While this invention sounds quite fascinating, it's important to keep in mind that patents granted to companies don't always guarantee the creation of a finished product. However, let's delve into the details of this patent and imagine the potential uses if it were to come to fruition. According to the patent, these eyewear lenses would be specifically designed to provide optimal viewing of both external displays and displays in a head-mounted device, all while protecting the user's eyes from the sun. To achieve this, the lenses would include a polarizer and a color filter customized for a particular target display. For displays emitting linearly polarized light, the lenses would incorporate a linear polarizer. On the other hand, for displays emitting circularly polarized light, the lenses would utilize a circular polarizer, which would consist of a quarter wave plate and a linear polarizer. Additionally, the color filter would be tailored with peak transmission spectrum curves that correspond to the primary colors of the target display. This would allow for optimal preservation of color and brightness from the display, while effectively reducing the brightness of sunlight. If Apple were to develop this eyewear, the potential applications could be vast. Imagine being able to effortlessly view important information directly on your sunglasses while still protecting your eyes from harmful UV rays. This technology could revolutionize outdoor activities, such as hiking or cycling, by providing real-time data without needing to look at a separate device. However, it's crucial to recognize that patents often remain just ideas, and not all concepts make it to the production stage. So, while this patent showcases the innovation and forward-thinking of Apple, it remains to be seen if and when such eyewear will hit the market. What are your thoughts on this concept? Can you envision yourself using display-optimized sunglasses? How would you incorporate this technology into your daily life? Share your insights in the comments below.
Eyewear such as sunglasses may include display-optimized lenses. The lenses may be optimized for viewing an external display and/or for viewing a display in the head-mounted device while also providing sun protection for the user's eyes. The lenses may include a polarizer and a color filter that are designed for a given target display. Lenses that are optimized for a display that emits linearly polarized light may include a linear polarizer. Lenses that are optimized for a display that emits circularly polarized light may include a circular polarizer. The circular polarizer may include a quarter wave plate and a linear polarizer. The color filter may have a transmission spectrum curve with peaks corresponding to the primary colors of the target display so that the color and brightness of display light is preserved while the brightness of sunlight is reduced
US Patent 11803060
Apple Inc.
Wearable Electronic Devices Protect Components from Elements in External Environment
What is this invention?
Watch with sealed housing and sensor module
A wearable electronic device, so neat
Can provide a seal member to keep it complete
It forms a fluid barrier, not hard to see
To protect components from the elements of the sea
The sensor modules and flex circuits are connected with glee!
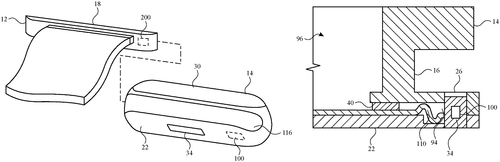
In a recent patent application, Apple Inc. has described a potential innovation in wearable technology that could protect the internal components of electronic devices, such as smartwatches, from external elements. The patent suggests the use of a seal member to create a fluid barrier between the inner chamber and the outer environment. One of the key advantages of this invention is the ability to safeguard sensitive components from external factors like water ingress. By creating a barrier, the sealed inner chamber ensures the durability and functionality of the device. Additionally, the outer chamber can accommodate sensor modules and other components, extending the capabilities of the wearable. While this patent showcases Apple's dedication to improving their wearable technology, it's important to note that not all patented ideas make it to the market as actual products. However, if Apple were to implement this feature in their future smartwatches, it could gain an edge over competitors in terms of durability and functionality. Imagine the potential uses of a smartwatch equipped with a fluid barrier. Outdoor enthusiasts would no longer have to worry about their device getting damaged during water-based activities, while fitness enthusiasts could track their performance underwater. The seal member may also pave the way for innovative designs and customization options, allowing users to choose different watchbands that interact seamlessly with the watch housing. Although this patent is still in the conceptual phase, it raises intriguing possibilities for the future of wearable technology. Do you think the addition of a fluid barrier would significantly enhance the functionality of smartwatches? Share your thoughts in the comments below.
The text describes a wearable electronic device, such as a watch, that can provide a seal member to form a fluid barrier between an inner chamber therein and outer chambers. Components within the sealed inner chamber can be protected from elements from the external environment (e.g., water ingress, etc.). The components outside of the inner chamber can include sensor modules and the like. Such components can be operatively connected to components within the inner chamber, for example, by a flex circuit that extends across the seal member.
US Patent 11803162
Apple Inc.
Power converter circuit included in computer system analyzes demand current to adjust voltage
What is this invention?
Current measurement for power converter circuits
A power converter circuit was found,
In a system with a sample and phase round.
The voltage level it did compare,
To the reference voltage there,
So its operation could be soundly bound!
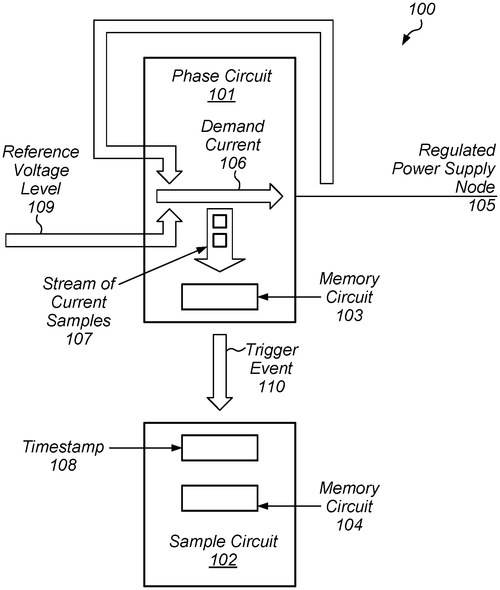
In a recent patent application by Apple Inc., a power converter circuit for computer systems is described. This circuit consists of two key components: a phase circuit and a sample circuit. The phase circuit compares the voltage level of the regulated power supply node with a reference voltage to generate a demand current. This demand current is then utilized to adjust the voltage level of the regulated power supply node. But what sets this patent apart is its ability to go beyond simple power regulation. The phase circuit also digitizes the demand current, converting it into a bit stream, which is then stored in a memory circuit. On the other hand, the sample circuit generates timestamp information that points to specific storage locations in the memory circuit. These storage locations correspond to trigger events, allowing for analysis of the power converter circuit's operation under different circumstances. Additionally, this data analysis capability enables the adjustment of operating parameters for optimal performance. While the patent may sound intriguing, it is crucial to remember that not all patented technologies make their way into actual products. However, if Apple were to develop and implement this power converter circuit, it could potentially enhance the efficiency and performance of their computer systems. Competing companies in the technology market also offer similar power converter circuits, but it remains to be seen how Apple's approach would differentiate itself from these existing solutions. Moreover, the potential applications of this technology extend beyond computer systems. It could potentially be utilized in various electronic devices that require power conversion. What are your thoughts on Apple's patent for this power converter circuit? Do you believe this technology has the potential to revolutionize power management in electronic devices? Share your insights in the comments below.
This text describes a power converter circuit that is included in a computer system. The power converter circuit includes a phase circuit and a sample circuit. The phase circuit compares the voltage level of the regulated power supply node to the reference voltage to generate the demand current, which is then used to adjust the voltage level of the regulated power supply node. The sample circuit generates timestamp information that points to particular storage locations in the memory circuit that correspond to trigger events, allowing analysis of the operation of the power converter during different circumstances as well as adjustment of operating parameters.
US Patent 11803219
Apple Inc.
Touch detection using depth images
What is this invention?
IMU for touch detection
A touch detected, data from IMU
It monitors movement of the touching few
Accelerometer tracks it true
Depth image captures view
For a response to perform an operation too.
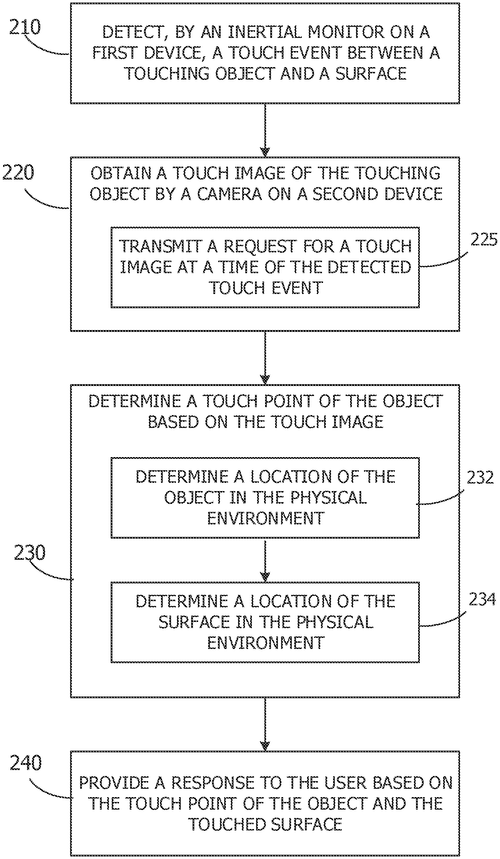
In a recent patent application, Apple Inc. has outlined a potentially groundbreaking technology that could revolutionize the way we interact with touchscreens. The patent details a touch detection system that combines data from an Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) with a depth image captured by a separate device, allowing for more precise touch recognition. While the patent is undoubtedly intriguing, it is important to remember that not all filed patents become fully realized products. Many companies, including Apple, file patents regularly to protect their intellectual property and explore various avenues of innovation. Therefore, it remains uncertain whether this touch detection system will make its way into the hands of consumers. That being said, if Apple were to develop and commercialize this technology, it could potentially enhance user experiences on their devices. By incorporating IMU data and depth images, the touch detection system could offer greater accuracy and responsiveness, allowing for more seamless interaction with touchscreens. It is not difficult to envision how this technology could be used in a range of applications, from gaming to drawing and beyond. In the ever-evolving landscape of touchscreen technology, competitors like Samsung and Google have also introduced their own unique features and functionalities to enhance user experiences. It will be interesting to see how Apple's potential touch detection system stacks up against existing technologies and how it could stand out from the crowd. Ultimately, the question lingers: Will Apple turn this patent into a reality? Only time will tell. In the meantime, we can speculate and imagine the possibilities of this technology. How do you think this touch detection system could improve your interactions with touchscreens? Let us know in the comments below.
Touch detection may include determining, based on data from an IMU on a first device that monitors movement of a touching object, a touch event, wherein the touch event indicates contact between the touching object and a surface. The touch event may be detected by using an accelerometer or other sensor to track movement of the touching object. Then, the depth image captured by the second device may be obtained. The touch image may be used to determine the touch point of the object. And then, based on this information, a response (e.g., action) can be provided for performing an operation on behalf of the user who touched/moved/gestured at that particular location in space.
US Patent 11803233