Most innovative companies for 10/10/2023 (new inventions)
Exciting new inventions from Micron Technology, Inc., International Business Machines Corporation, Apple Inc., Google Llc And Amazon Technologies, Inc.
This is a weekly article summarizing a handful of inventions from the most innovative companies in the world. The summaries are created by an A. I. and proof-read by a human before publication. Attempts are made to ensure accuracy of the descriptions, but it is very much a work in progress. Each invention description is preceeded by a poem about the invention that is written by the A. I. I have found the limerick is actually quite good at explaining the invention in simple terms. Enjoy!
****
New Installation Tool Helps You Accurately Measure and Affix Objects to Vertical Surfaces
What is this invention?
Installation tool for affixing objects to a plurality of vertical surfaces and methods using thereof
There's a tool for affixing things,
A body with two elongated wings.
It has scales on the front and rear,
Plus two end-stops to make it appear
That attaching objects is made quite simple here!
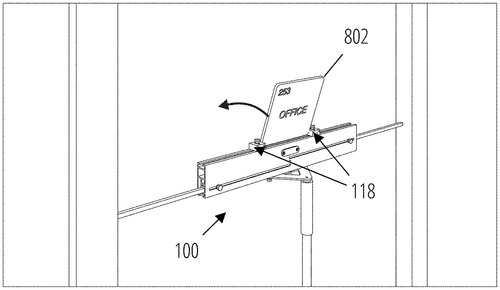
In an intriguing new patent, a company has described various embodiments of an installation tool for affixing objects to a multitude of vertical surfaces. The tool features a rigid and elongated rectangular body, with a front and rear flat surface that incorporates a measurement scale for acquiring reference installation measurements. It also includes a bubble level for ensuring accuracy and two elongated arms that can be extendable from either end. One interesting aspect of this tool is its clever design, allowing users to easily adjust and secure the end-stops along the top channel of the body. These end-stops not only provide stability but also offer a means to releasably secure the tool at various positions during installation. Additionally, a support mount is included, which can be fastened to an extendable vertical support member, adding versatility to the tool's usage on different surfaces. While the patent's described installation tool showcases innovative features, it is important to note that a patent filing does not guarantee the invention will become a marketable product. It is common for companies to file patents as a means to protect intellectual property and inventions, without necessarily following through with commercialization. That being said, if this installation tool were to materialize, it could potentially find various applications in construction, interior design, and DIY projects. Imagine using this tool to hang artwork or shelves on a wall, ensuring precise measurements and level alignment every time. The extendable arms and vertical support mount may also prove useful for mounting objects on uneven surfaces, such as brick or stone walls. However, it remains to be seen whether this concept will ever make it to the market. Many factors come into play, including manufacturing costs, market demand, and competition from existing products. Speaking of competition, other installation tools, such as laser-guided levels or digital measuring devices, already exist in the market. Therefore, the inventors of this particular tool would need to find a way to stand out and justify its place amongst its competitors. Considering all aspects, do you believe this installation tool has the potential to revolutionize the way we affix objects to vertical surfaces? Would you find it useful in your own projects? Share your thoughts in the comments below!
This document describes various embodiments of an installation tool for affixing objects to vertical surfaces. The tool includes a body that extends longitudinally according to a first axis, and has a front flat surface and a rear flat surface. There is also a measurement scale on the front and rear flat surfaces, which can be used to acquire reference installation measurements. Additionally, the tool includes two elongated arms that are reversibly extendable from one of the end flat surfaces along the first axis. Two end-stops are also included, each end-stop configured to be slidingly movable along a top channel of the body and comprising securing means thereon to releasably secure it at a position along said top channel. Finally, the support mount is also included, which can have fastened thereto an extendable vertical support member. This allows for easy attachment of objects to vertical surfaces using this installation tool.
US Patent 11781850
****
Alignment Tool Keeps Pile Cap Tensioned
What is this invention?
Alignment tool
A tool for pile caps was disclosed,
It had a tensioner and cord guide enclosed.
The fastener was coupled to the tensioner too,
To keep the cord under tension true.
This alignment tool will be sure to please,
For all your construction needs!
In a recently published patent, an alignment tool for a pile cap has been unveiled. The tool consists of several components, including a tensioner, a pile cap fastener, and a cord guide. The tensioner is designed to apply tension to a cord, while the fastener is attached to the tensioner. The cord guide, which is coupled to the fastener, facilitates the smooth movement of a cord under tension by the tensioner. The alignment tool presents an interesting concept that could potentially streamline construction processes involving pile caps. Pile caps are structural elements used to connect piles, which are deep foundational supports, to the superstructure of a building or bridge. Ensuring the proper alignment of pile caps is crucial to maintain the structural integrity of the entire project. Although the patent demonstrates the inventors' innovative thinking, it is important to remember that not all patented ideas go on to be transformed into marketable products. The technology landscape is crowded with various solutions designed to address similar alignment challenges in the construction industry, such as laser alignment systems and digital surveying tools. If this alignment tool were to become a reality, its potential uses could range from large-scale construction projects to infrastructure maintenance and repair. The efficiency and accuracy provided by the tool could potentially save time and resources for builders and engineers. However, questions remain about the practicality, cost-effectiveness, and scalability of the proposed invention. Will it be able to compete with existing solutions? How will it fare in different types of construction environments? What challenges might arise in real-world implementation? The patent may be just the beginning for this alignment tool, and it will be interesting to see how it evolves and whether it will be embraced by the construction industry. Do you think the implementation of such a tool would offer significant benefits to construction processes? Share your thoughts in the comments below.
The disclosed alignment tool for a pile cap comprises a tensioner, a pile cap fastener, and a cord guide. The tensioner is configured to apply tension to the cord, while the fastener is coupled to the tensioner and is configured to attach the cord guide to the fastener. The cord guide is configured toguide the cord under tension by the tensioner.
US Patent 11781851
****
New Surface Sensing Apparatus Reveals Speckle Patterns
What is this invention?
Surface sensing probe and methods of use
A surface sensing apparatus was made
With a source of radiation to aid
An emission deviation facility, too
For the second speckle pattern view
And sensors that measure two states with precision grade.
In a recently published patent, a surface sensing apparatus has been described that could potentially revolutionize the way we interact with our environment. The apparatus utilizes coherent radiation emissions to create illumination states and speckle patterns on a surface, which are then sensed by a specialized sensor. At first glance, this invention seems like a remarkable step forward in the field of surface sensing technology. By utilizing coherent radiation, the apparatus is able to generate precise and detailed speckle patterns, allowing for accurate representation of the surface's properties. This could have significant implications in various industries, including manufacturing, construction, and even healthcare. Imagine a construction worker using this apparatus to quickly assess the quality of a concrete surface on a building site. With a simple scan, they would be able to determine if any flaws or imperfections exist, allowing for immediate corrective action. Similarly, medical professionals could potentially use this technology to detect irregularities in the skin during dermatology exams, or to analyze tissue samples in a non-invasive manner. However, it is important to note that this patent is merely a conceptualization of an apparatus and its potential uses. While the idea is undoubtedly intriguing, it is not yet clear whether the invention will actually materialize into a practical product. Many patents never make it past the patenting stage, and even if they do, the process to develop a commercial product can be long and complex. Furthermore, the patent does not discuss any specific competitors or existing products in the market. It is crucial to consider the current landscape of surface sensing technologies and their limitations before fully understanding the potential impact of this invention. With that in mind, what are your thoughts on this patent? Do you believe this surface sensing apparatus has the potential to revolutionize various industries? Or do you think it is unlikely to progress beyond the conceptual stage? Share your insights and opinions in the comments below.
The surface sensing apparatus disclosed herein includes a source of coherent radiation capable of outputting wavelength emissions to create a first illumination state to illuminate a surface and create a first speckle pattern, an emission deviation facility capable of influencing the emission to illuminate the surface and create a second illumination state and a second speckle pattern, and a sensor capable of sensing a representation of the first and a second speckle intensity from the first and second speckle pattern. Additionally, methods are disclosed for sensing properties of the surface having either one or two different surface states. In one embodiment, this is accomplished by illuminating the surface with the source of coherent radiation in order to create the first illumination state. Then, based on how well the emitted light matches up with what was sensed from the surface in terms of speckle intensity, an influence can be applied to alter (or "deviate") how much light is emitted in order to achieve desired results for creating the second illumination state. Finally, using another sensor it is possible to measure (and represent) both Speckle Intensities as they exist in each respective illumination state. Thus allowing for very accurate measurements across multiple dimensions when trying to understand or characterize some property or phenomenon associated with or affecting said surface.
US Patent 11781855
****
Predictive Traffic Law Enforcement Profiler: Keep Ahead of the Speed Trap
What is this invention?
Method and apparatus for utilizing estimated patrol properties and historic patrol records
A predictive traffic law enforcer
Apparatus that's really much smarter
It'll tell you the speed
Where cops are to heed
So no fines or citations occurr-er
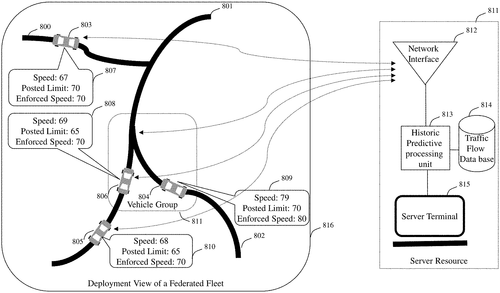
In a recent patent filing, a new invention has caught our attention: the Predictive Traffic Law Enforcement Profiler. This innovative technology aims to revolutionize the way drivers navigate through traffic and interact with law enforcement. The Predictive Traffic Law Enforcement Profiler apparatus and method claims to employ a variety of data sources, such as historic traffic law enforcement records, crowd-sourced reports, and historical traffic data to provide drivers with real-time information. By incorporating location, time, and velocity, this invention aims to help drivers stay informed about enforced speed limits, enforcement profiles, and the schedules and locations of traffic law enforcement officers. While the concept behind the Predictive Traffic Law Enforcement Profiler is intriguing, it is important to consider its practicality and feasibility as a consumer product. Although it offers the potential benefit of helping drivers avoid unnecessary traffic violations and speeding tickets, there are several issues that need to be addressed. Firstly, the information provided by the database must be accurate, up-to-date, and reliable. In addition, the apparatus must be technologically advanced and user-friendly enough for everyday drivers to understand and integrate into their navigation routines. Competitor products such as radar detectors and navigation apps already cater to drivers' needs for traffic information, but they do not include the comprehensive predictive capabilities proposed by this invention. However, it remains to be seen whether consumers would be willing to invest in a device solely focused on navigating law enforcement encounters. While it is exciting to envision the potential uses and benefits of the Predictive Traffic Law Enforcement Profiler, it is crucial to consider the practicality of turning this patent into a commercially viable product. Can such an invention truly deliver on its promises? What concerns or advantages do you foresee with this technology? Share your thoughts in the comments below.
The present invention provides a predictive traffic law enforcement profiler apparatus and method which incorporates a means to determine current location, time, velocity, and also incorporates a means to utilize a database derived from historic traffic law enforcement records, crowd sourced records and historical traffic data. The predictive processing means is used to provide historic traffic law enforcement records and estimates of enforced speed limits and enforcement profiles, patrol locations and schedules of traffic law enforcement to a driver. This information can be used by drivers in order to avoid potential fines or citations.
US Patent 11781883
****
Broadband light source with silicon photonics interrogator for scanning reflected light
What is this invention?
Reflected light wavelength scanning device including silicon photonics interrogator
A reflected light wavelength scanning device,
Was built with a circulator and precise.
It could separate the polarized light,
To be injected just right,
And its output was quite hard to surmise.
In the realm of advanced photonics technology, a recent patent has caught the attention of innovators and tech enthusiasts alike. The patented reflected light wavelength scanning device, featuring a cutting-edge silicon photonics interrogator, has piqued interest due to its potential for groundbreaking applications. The device is comprised of several key components: a light source module that emits broadband light, an optical sensor that receives the light output and selectively reflects light in a specific band to a circulator, and an interrogator that separates and injects polarized light from the reflected light input. The device's ability to utilize polarized light in this manner opens up exciting possibilities in the world of photonics. Imagine a scenario where this technology is harnessed for medical diagnostics. The device holds the potential to provide high-resolution imaging of biological tissues, enabling doctors to detect abnormalities or track the progress of diseases with greater precision. Additionally, it could be employed in environmental monitoring, allowing researchers to measure and analyze pollutants in real-time, aiding in the development of more effective environmental protection measures. While this patented device offers exciting opportunities, it is essential to acknowledge the challenges inherent in transforming it from concept to market-ready product. The field of photonics is highly competitive, with established players already offering similar technologies. Consequently, it remains to be seen whether this invention will overcome the hurdles to commercialization and find a place among its competitors. Nevertheless, the possibilities raised by this patent raise an interesting question: How might the integration of silicon photonics and reflected light wavelength scanning impact various industries? Could this innovation revolutionize fields like healthcare, telecommunications, or environmental science? Share your thoughts and speculations below in the comments section!
A reflected light wavelength scanning device is provided that includes a light source module for outputting broadband light, an optical sensor that receives light output from the light source module through a circulator, reflects light in a specific band to the circulator, and transmits light in a band other than the specific band, and an interrogator for selectively injecting the polarized light by separating the polarized light from the reflected light input through the circulator.
US Patent 11781888
Micron Technology, Inc.
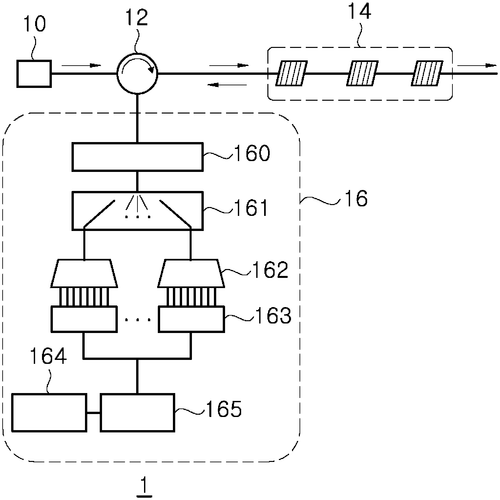
Temperature Sensors: Analog Core Provides Average Measurement
What is this invention?
Systems and methods for reducing temperature sensor reading variation due to device mismatch
A temperature sensor is made,
That's sure to be well displayed.
It has an analog core and a multiplexer too,
Plus a controller that'll take two readings for you.
The first reading taken while the multiplexer in one state,
And the second when it's in another - no need to wait!
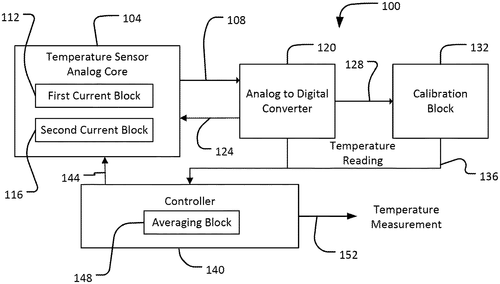
Micron Technology, Inc. has recently filed a patent for a temperature sensor that has the potential to revolutionize temperature measurement. The sensor consists of an analog core with two circuit nodes that can provide a temperature-dependent output. It is further equipped with a multiplexer that can be in various states, enabling the connection of different circuit elements to the two circuit nodes. Additionally, a controller is incorporated into the system to calculate the average temperature measurement based on two readings taken while the multiplexer is in different states. While this patent showcases an interesting approach to temperature sensing, it is important to note that it is still in the early stages of development. As with any patent, it is uncertain whether this invention will be brought to market or if it will remain solely a concept. It also remains to be seen how this technology would compare to existing temperature sensing products already offered by competitors. However, if this temperature sensor were to become a reality, it could find application in various industries. The ability to provide a more accurate average temperature measurement could be particularly beneficial in fields such as environmental monitoring, industrial manufacturing, and even healthcare. Having access to more precise temperature data could enable better decision-making and enhance safety protocols. In light of this patent, it would be interesting to hear from our readers about their thoughts on the future of temperature sensing technology. How do you envision this invention being utilized, and do you think it has the potential to outperform current industry offerings? Share your insights in the comments below.
A temperature sensor is disclosed that includes an analog core, a multiplexer, and a controller. The analog core has at least first and second circuit nodes and is configured to provide a temperature dependent output. The multiplexer is coupled to the first and second circuit nodes and is configured for at least first and second states in each of which the first circuit node couples to a different circuit element and in each of which the second circuit node couples to a different circuit element. The controller is coupled to the analog core and is configured to provide a temperature measurement that is an average of at least first and second readings of the temperature dependent output of the analog core, the first reading taken while the multiplexer is in the first state, and the second reading taken while the multiplexer is in the second state.
US Patent 11781918
Micron Technology, Inc.
Memory System Keeps Track of Data Writes
What is this invention?
Wear leveling for non-volatile memory using data write counters
A controller was tasked with a mission,
To scan the data write counters for selection.
It received some data to be stored,
And wrote it down on its first board.
The memory system then worked without any objection!
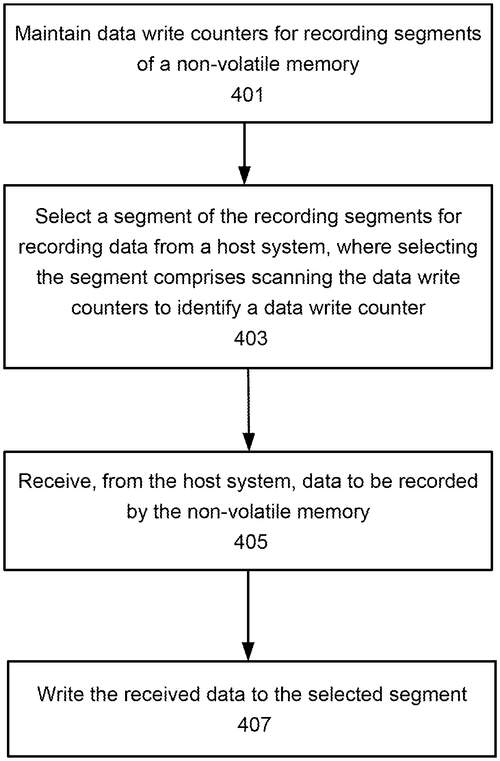
In a recent patent application, Micron Technology, Inc. has introduced a memory system that could potentially revolutionize data storage. The proposed system features a controller, such as a CPU, FPGA, or GPU, and recording segments within a non-volatile memory, such as a flash memory device. These recording segments are utilized by the controller to store data. What sets this memory system apart is its unique functionality. The controller is designed to maintain data write counters for each of the recording segments. When data is received from a host system to be recorded in the non-volatile memory, the controller scans the data write counters to select a specific segment. By identifying the first data write counter corresponding to the chosen segment, the received data can be efficiently written to its designated location. While this patent application showcases Micron Technology's commitment to pushing the boundaries of memory storage, it's crucial to bear in mind that not every patent becomes a commercially available product. The tech world is filled with brilliant ideas and exciting innovations, but only those that prove to be feasible and practical are transformed into tangible consumer offerings. Considering the competitive landscape in the memory storage industry, where key players like Samsung and Western Digital already dominate the market with their own breakthroughs, it remains to be seen how Micron's memory system will fare. However, if successfully developed, this technology could find wide-ranging applications in various sectors, including data centers, smartphones, and even autonomous vehicles. As we eagerly await the future unfoldings of Micron Technology's patent, we can't help but wonder: How do you envision this memory system being utilized? Do you see it making a significant impact in the tech industry? Leave your thoughts and predictions in the comments below.
The text describes a memory system that maintains data write counters. The controller selects a first segment of the recording segments for recording data from a host system, wherein selecting the first segment comprises scanning the data write counters to identify a first data write counter corresponding to the first segment. The controller then receives data to be recorded by the non-volatile memory and writes it to the selected first segment.
US Patent 11782605
Micron Technology, Inc.
Memory Units With Fewer Writes Can Be Weighed Down
What is this invention?
Scanning techniques for a media-management operation of a memory sub-system
A document that describes memory management,
Including techniques for a wear-leveling plan.
Identifying first quantities of write counts,
For SMUs in the mapped region, no doubt.
To perform the operation with least stress and strain,
The fewest quantity of writes must be found!
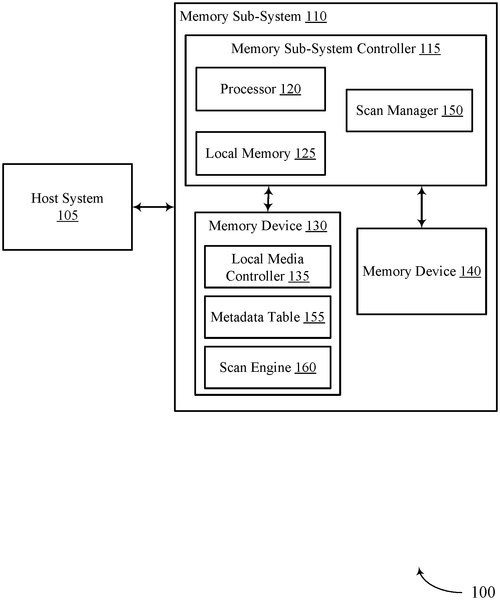
In a recent patent application, Micron Technology, Inc. has proposed a set of methods, systems, and devices to enhance the performance and longevity of memory. The innovation aims to tackle the issue of wear and tear on memory units, which can lead to data corruption and system failure over time. According to the patent description, this technology involves identifying the number of write counts for a group of super management units (SMUs) in a specific part of the memory sub-system. By analyzing this data, the hardware component can determine which SMU has the fewest write counts, indicating that it has been subjected to less wear compared to the others. The system can then perform wear-leveling operations to distribute the workload evenly across the memory subsystem, ensuring more balanced usage and preventing premature failure. The potential applications for this technology are promising. In a world dominated by data-intensive applications and rapidly evolving technologies, memory performance is crucial. By implementing wear-leveling techniques, Micron's invention could lead to more reliable and durable memory systems, benefiting consumers and enterprises alike. Imagine having a smartphone or a computer that can handle intensive tasks without sacrificing speed or reliability, thanks to this innovation. However, it is worth noting that this is just a patent application, and there is no guarantee that the technology will be developed into a tangible product. While Micron is a reputable technology company known for its memory solutions, it is essential to be pragmatic when evaluating the likelihood of a patent becoming a commercial reality. Moreover, competition in the memory market is fierce, with established players like Samsung and SK Hynix constantly pushing the boundaries of what is possible. It remains to be seen whether Micron's invention will give them a competitive edge or if their rivals will come up with even more groundbreaking solutions. In conclusion, Micron's patent application for memory wear-leveling techniques shows promise in addressing the challenges of data degradation and system failures. However, as with any patent, the path from invention to a marketable product is uncertain. For now, we can only hope that this innovation or a similar one will materialize and provide us with more reliable and durable memory solutions. What do you think about the future of memory technology? Will innovations like wear-leveling become commonplace, or are there other challenges that need to be addressed? Share your thoughts in the comments below.
This document describes methods, systems, and devices for memory management. The memory management can include techniques for identifying first quantities of write counts for a first plurality of super management units (SMUs) in a mapped region of a memory sub-system. The hardware component can then identify a first SMU of the first plurality that includes the fewest quantity of write counts. Based on this information, the wear-leveling operation can be performed based at least in part on the first quantity of write counts being less than the second quantity of writes counts.
US Patent 11782606
Micron Technology, Inc.
Memory Devices Enable Error Detection and Reporting for Extended Power Saves
What is this invention?
Error information signaling for memory
A memory device in power-save,
Detected errors that it could not waive.
It then signaled the host,
And per command did boast,
Exiting its mode with no deprave.
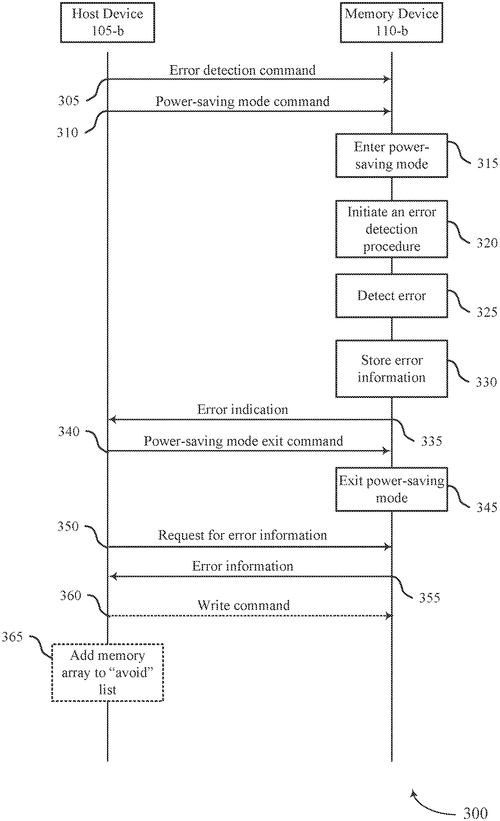
Micron Technology, Inc. has recently filed a patent for methods, systems, and devices that aim to enhance error information signaling for memory. The proposed invention involves a memory device that can perform an error detection procedure while in a power-saving mode. If an error is detected, the memory device will signal the error to a host device. Upon receiving this indication, the memory device will exit the power-saving mode and enable its interfaces. It will then be capable of transmitting error information to the host device upon request. While this patent may seem like a technical solution to a relatively niche problem, it is important to consider the potential applications it could have. In theory, this innovation could be invaluable in scenarios where power efficiency is paramount, such as in mobile devices or Internet of Things (IoT) devices. Competitor products currently on the market focus primarily on error detection and correction, but rarely offer seamless integration into power-saving modes. Micron's patent, however, describes a streamlined process that not only detects errors but also efficiently notifies the host device, seamlessly transitioning out of power-saving mode to transmit error information. Although this invention presents a promising technological advancement, it is essential to remember that securing a patent does not guarantee its commercialization. Many patented concepts never make it to production, and the fate of this innovation remains uncertain. Considering the potential benefits of this patent, it's worth pondering how it could revolutionize power-saving capabilities in various industries. How do you envision this technology being implemented? Could it be a game-changer in the mobile or IoT market? Share your thoughts and speculations in the comments below.
Methods, systems, and devices for error information signaling for memory are described. A memory device may perform an error detection procedure while in a power-saving mode. Upon detecting an error, the memory device may indicate the error to a host device. In response to indicating the error, the memory device may receive a command to exit the power-saving mode. The memory device may comply with the command and exit the power-saving mode by enabling one or more interfaces of the memory device. The memory device may receive a request for error information over the one or more interfaces and, in response to the request, may transmit the error information to the host device.
US Patent 11782608
Micron Technology, Inc.
Memory System Allows Fast Data Migration
What is this invention?
Systems, devices, techniques, and methods for data migration
A memory system that's quite clever,
Data migration it can deliver.
It'll transfer data fast,
From one device to the past,
Using two types of tech - how they quiver!
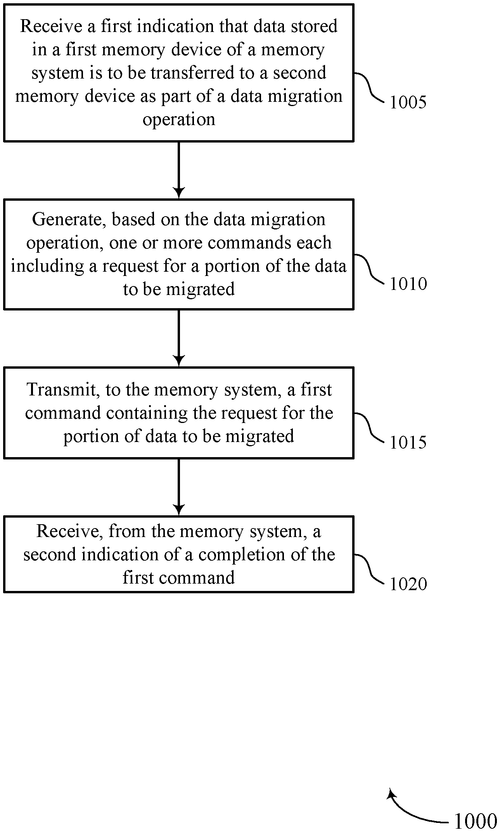
Micron Technology, Inc. has recently filed a patent for a new method of data migration operations using a memory system. The company's innovation revolves around the transfer of data between two different memory devices within the system, without the need for a host device. The patent describes a data migration component, possibly a driver, that enables the smooth transfer of data between a first memory device, which boasts a faster access speed, and a second memory device with a larger capacity. This innovative component communicates the data migration operation to a controller within the memory system, triggering the initiation of the data transfer. While this patent seems to be an intriguing development in the field of memory systems, it is important to note that many patents never actually make it to the production stage. As a writer who covers emerging technologies, it is crucial to maintain a level of skepticism when evaluating the real-world potential of such inventions. Existing memory systems and devices from competitors may provide similar functionalities for data migration, making it imperative for Micron Technology to showcase why their method stands out. Potential applications for this technology could include seamless data transfer between different memory technologies, resulting in improved data access and storage capabilities. However, it is essential to question whether the benefits provided by this invention outweigh the costs associated with implementing it. Will this technology be embraced by consumers and industry professionals? Or will it become just another patent filed away in the annals of memory system advancements? What are your thoughts on this new patent from Micron Technology, Inc.? Do you believe it has the potential to revolutionize data migration operations? Share your opinions and insights in the comments below.
This document describes methods, systems, and devices for performing data migration operations using a memory system. The memory system may include a data migration component, such as a driver, for facilitating the transfer of data between a first memory device that may implement a first memory technology (e.g., having a relatively fast access speed) and a second memory device that may implement a second memory technology (e.g., having a relatively large capacity). The component may indicate the data migration operation to the second component (e.g., controller) of the memory system. The second component may initiate the transfer of data between the first memory device and the second memory device based on receiving indication of the data migration operation. In some cases, the transfer of data between the first memory device and the second memory device may occur within thememory system without being transferred through host devices.
US Patent 11782626
International Business Machines Corporation
Get your drink on – with this nifty new invention!
What is this invention?
Bridging liquid between microfluidic elements without closed channels
A method of processing a filtered liquid,
A microfluidic device was given:
The filtering medium must be placed right,
So that the flow path is in sight.
Compress the medium and extract the volume, then process it with ease - its solution!
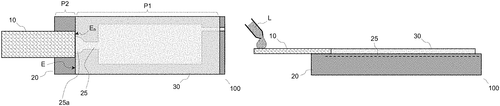
In a recent patent filed by International Business Machines Corporation (IBM), an intriguing method of processing filtered liquid with a microfluidic device has been described. The patent details a process that involves positioning a porous filtering medium in relation to the microfluidic device, allowing a flow path between the two. A liquid is then introduced into the filtering medium, where it advances along and undergoes filtration. To extract a specific volume of the filtered liquid, compression is applied to the filtering medium, enabling the extracted volume to reach the microfluidic device's channel via the flow path. Finally, the extracted volume is processed within the microfluidic device. While this patent showcases a potentially innovative approach to liquid filtration and processing, it should be noted that the existence of a patent does not guarantee the development of a commercial product. Often, such patents serve as a means to protect intellectual property and may not materialize as a market-ready invention. However, if this method were to be realized as a product, numerous applications could be imagined. For instance, it could find utility in medical diagnostics, where precise and efficient liquid processing is vital. Furthermore, it could facilitate advancements in biological research, environmental testing, or even industrial processes that require effective liquid filtration. In terms of competition, the market for microfluidic devices already has several players offering various solutions. Companies like Fluidigm and Bio-Rad Laboratories have established themselves in this field, supplying integrated fluidic circuits and microfluidic systems. It remains to be seen whether IBM's patented approach can differentiate itself and gain traction in this competitive landscape. With this in mind, readers are invited to ponder the potential impact and feasibility of this invention. Could a method for processing filtered liquid in a microfluidic device revolutionize a specific industry or create entirely new opportunities? Share your thoughts in the comments below.
The present invention is embodied as a method of processing a filtered liquid with a microfluidic device. The method includes positioning a porous filtering medium with respect to the microfluidic device, so as to allow a flow path between the filtering medium and a channel of the microfluidic device. The method further includes introducing a liquid in the porous filtering medium for the liquid to advance along the filtering medium and be filtered by the medium. The method further includes applying compression to the filtering medium to extract a given volume of the filtered liquid from the filtering media, where the extracted liquid volume reaches said channel via the flow path. The method further includes processing t he extracted volume with th e microfluid ic device
US Patent 11781954
International Business Machines Corporation
Detecting Objects With New Sensor Data
What is this invention?
Indoor intrusion detection
A computer-implemented way,
To detect objects in space one day;
Anemometers placed,
Data is then traced,
And an object's vector they can display!
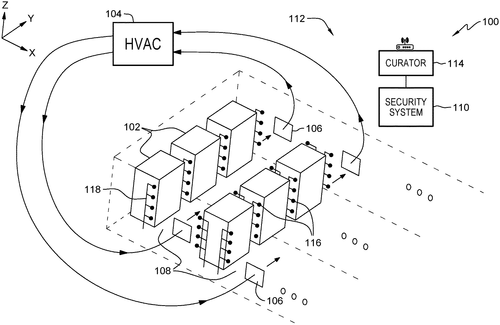
In a recent patent application, International Business Machines Corporation (IBM) has revealed a computer-implemented method, system, and computer program product for detecting objects. The innovation involves leveraging a network of anemometers strategically positioned throughout a space to gather sensor data on airflow. The method starts by receiving initial sensor data from the anemometers, which is then used to create a baseline profile of airflow within the space. Subsequently, the system receives second sensor data from the anemometers at a different time than the first sensor data. By comparing the second sensor data with the baseline, the method determines the presence of an object by identifying first different data. In response to detecting differences in the sensor data, the system generates a representation of the object using the first different data and corresponding location information. Additionally, the method calculates a vector associated with the object to further characterize its properties based on the identified differences. This patent application signals IBM's interest in developing a technology capable of detecting objects by analyzing changes in airflow patterns. While the concept is intriguing, it is important to consider the practicality of such a system becoming a marketable product. Competing technologies, such as computer vision-based object detection systems, have gained significant traction in applications ranging from security to autonomous vehicles. Comparatively, leveraging anemometers may face limitations, as their effectiveness could be hindered by factors like air fluctuations, interference, and the requirement for extensive sensor network installation. That being said, there may be potential applications for this technology, especially in environments where visual-based detection is less viable, such as areas with low visibility or high levels of dust or smoke. It could potentially be used in industrial settings or hazardous environments where airflow changes can be indicative of the presence of objects or anomalies. Ultimately, the success of this technology will rely on its ability to overcome the aforementioned challenges and offer clear advantages over existing solutions. It remains to be seen if IBM will develop this concept further and bring it into the market. What are your thoughts on this concept? Can you imagine any practical applications for such a system? Share your opinions in the comments below!
The invention provides a computer-implemented method, system, and computer program product for detecting objects in a space. The method can include receiving first sensor data from a plurality of anemometers positioned throughout the space, creating a baseline profile of airflow in the space based on the first sensor data, and receiving second sensor data at a different time than the first sensor data. The method can include comparing the second sensor data with the first sensor data to determine first different data. In response to determining that the second sensor data is different from the first sensor data, a representation of the object using the first different data and first location data related to the first differentdata can be rendered. Additionally, a vector associated with the object can be calculated using the first differentdata andthefirstlocation datad.
US Patent 11782068
International Business Machines Corporation
A Method and a Computer System for Asymmetric Replication that Enhances Performance
What is this invention?
Efficient use of optional fast replicas via asymmetric replication
A method and system have been found
For replicating data asymmetrically 'round.
The first copy is reliable, stored slow,
Reads preferentially for enhanced speed to show;
Should a write operation fail on the first go,
Then a stale label will be set in tow.
In a recently published patent, International Business Machines Corporation (IBM) has proposed a method and computer system for asymmetric replication of data. The patent outlines a storage system that organizes data in two copies, with the second copy stored in non-volatile storage and designed to be read at a slower speed than the first copy. The goal of this approach is to achieve enhanced performance speed by preferentially performing read instructions via the first copy. While the patent itself does not explicitly mention any competitor products, this concept of asymmetric replication bears similarity to existing technologies such as data mirroring and redundancy systems. These technologies aim to ensure data availability and reliability in case of failures or crashes. The potential applications for this technology are vast. Industries that heavily rely on real-time data processing, such as finance and telecommunications, could benefit from improved performance and responsiveness offered by the asymmetric replication system. Additionally, organizations that handle large amounts of critical data, such as government agencies or healthcare providers, could potentially leverage this innovation to enhance their data protection and recovery capabilities. As with any patent, it is important to note that not all innovations make it into actual products. Many patents are filed as a means to protect intellectual property or explore future possibilities. While IBM's proposed method for asymmetric replication of data shows promise, it remains to be seen whether this concept will be developed further and eventually Commercialized. What are your thoughts on this patent? Do you believe that asymmetric replication could become a standard practice in data storage systems? Share your opinions in the comments below.
The method and computer system provide for asymmetric replication of data. The first copy is reliable and stored so as to be readable at a speed slower than for the second copy. A read instruction regarding the set of data is received and performed preferentially via the first copy such that the asymmetric replication achieves enhanced performance speed. If a write operation fails on the first copy, then a stale label is set for the first copy.
US Patent 11782630
International Business Machines Corporation
Backend Storage System Keeps House Clean
What is this invention?
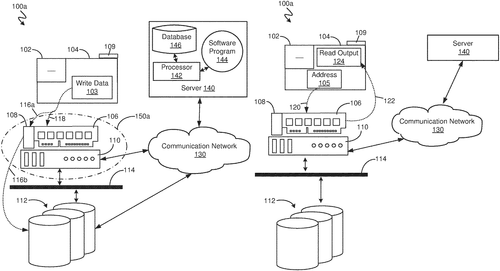
Backend aware virtualized storage
A backend storage system was detected,
With a virtualization to ensure it's protected.
Data is transferred for storage and retrieval,
Commands issued by the virtualized model.
Overhead conditions are checked with precision,
To prevent any more housekeeping operations in succession.
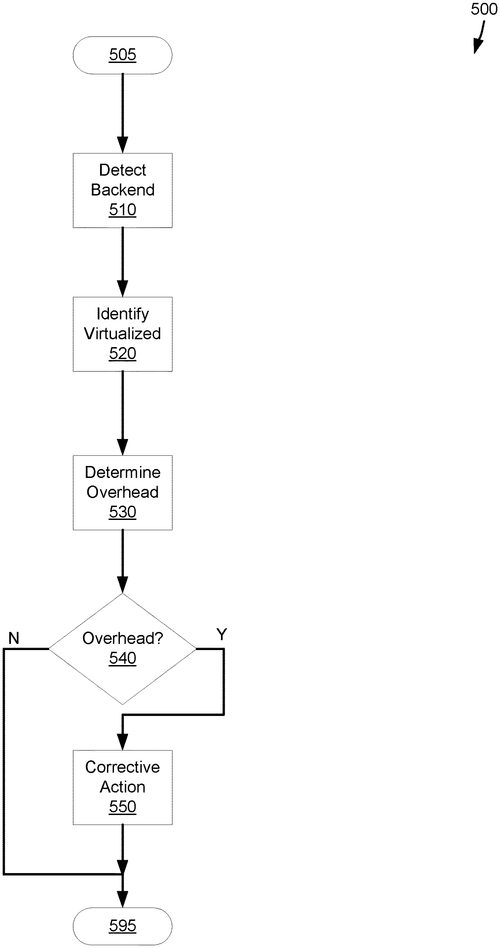
In a recent patent application, International Business Machines Corporation (IBM) introduces a new storage virtualization system that aims to optimize backend housekeeping operations in a backend storage system. While the patent description may sound technical, the concept behind it is quite interesting. The storage virtualization system detects and identifies backend housekeeping operations related to a specific portion of the storage system. It then transfers data to and from the backend storage system while issuing commands to ensure smooth operation. Additionally, the system identifies virtualized operations related to a specific portion of the storage virtualization system. By evaluating the storage overhead condition based on these operations, the system can take corrective actions that prevent the potential performance issues caused by additional backend housekeeping operations. At a glance, this patent suggests a solution to streamline storage management processes, ultimately improving performance and efficiency. Currently, various storage solutions offered by competitors, such as EMC and NetAp. p, focus on optimizing storage capacities and speeds. IBM's approach, however, appears to address a crucial aspect of backend operations that may have been overlooked. While the potential uses for this technology are broad, it remains uncertain whether or not IBM plans to transform this innovative concept into a market-ready product. As with any patent, there are no guarantees that it will make its way beyond the application stage. However, if successful, this storage virtualization system could have significant implications for industries reliant on efficient data storage and retrieval. What do you think? Could this patent signal a game-changer in storage system optimization? How would you envision its practical implementation? Share your thoughts in the comments below.
A first backend housekeeping operation of a backend storage system is detected by the storage virtualization system. The first backend housekeeping operation is related to a first backend storage portion of the backend storage system. The storage virtualization system transfers data to the backend storage system for storage and retrieval. The storage virtualization system issues commands to the backend storage system. A first virtualized operation related to a first virtualized storage portion of the storage virtualization system is identified. Astorage overhead condition is determined based on the firstbackend store portion and based on the first virtualized operation. A corrective action is performed based onthestorage overhead condition preventing potential performance of one or more additional back end house keeping operations
US Patent 11782641
International Business Machines Corporation
Create Variable Replaced AI Accelerator Code with This System
What is this invention?
Variable replacement by an artificial intelligence accelerator
A system for AI acceleration
Was created with great elation.
It had a memory and processor too,
Which helped create an AI view.
For the template code to replace,
The variables it could ace!
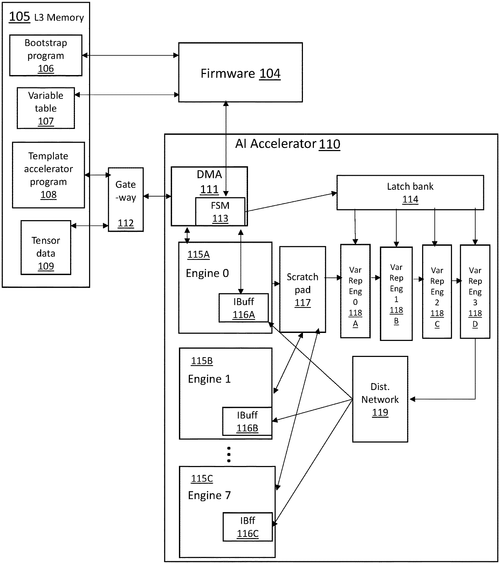
International Business Machines Corporation (IBM) has recently been granted a patent for an intriguing system that aims to simplify the development of artificial intelligence (AI) accelerators. The patent describes a system for variable replacement in a template AI accelerator code. The system consists of several components: at least one memory, at least one processor, and an AI accelerator. The processor is responsible for computing a table of variables from a template AI accelerator code, while the AI accelerator, equipped with a series of engines, is tasked with creating a variable-replaced AI accelerator code by substituting the variables with actual values from the computed table. This patent raises interesting possibilities for the AI industry. Simplifying the development process for AI accelerators could potentially expedite the creation of cutting-edge AI technologies. With the variable replacement system, developers may be able to efficiently customize AI accelerators for different applications, potentially increasing their performance and versatility. This, in turn, could lead to more advanced AI systems that are optimized for specific tasks. However, as with any patent, it is important to consider the practicality of implementing this technology. Although the concept represents an innovative approach to accelerate AI development, the actual production and commercialization of such a system can face numerous challenges. The potential complexities of integrating the variable replacement system into existing AI frameworks, as well as the need for specialized hardware, may limit its widespread adoption. Moreover, it is crucial to take into account the current landscape of AI accelerators. Competing products, like NVIDIA's GPUs or Google's Tensor Processing Units, have already established themselves as the go-to solutions for AI acceleration. Therefore, IBM's system for variable replacement will need to prove its superiority in order to attract attention and gain traction in the market. In conclusion, IBM's variable replacement system patent presents an exciting concept with the potential to streamline AI accelerator development. However, whether it will become a widely adopted commercial product remains to be seen. How do you think this invention could impact the future of AI? Share your thoughts in the comments below.
The text describes a system for variable replacement in a template artificial intelligence (AI) accelerator code. The system includes at least one memory, at least one processor communicatively coupled to the at least one memory, and configured for computing at least one table of variables from a template AI accelerator code. The AI accelerator includes a plurality of engines, and communicatively coupled to the at least one processor and the at least one memory. The AI accelerator is configured to create a variable replaced AI accelerator code for the plurality of engines of the AI accelerator from the template AI acceleration code by replacing variables in the template AI acceleration code with actual values from the at least one table of variables.
US Patent 11782683
Apple Inc.
Temperature Probe Reveals Hidden Secrets
What is this invention?
Temperature gradient sensing in portable electronic devices
A temperature sensing system was found
With a sensor and probe that abound
The thermopile ran 'cross the substrate's two ends
Measuring temps to the device's defense
From the first measured temp, a second could be sound
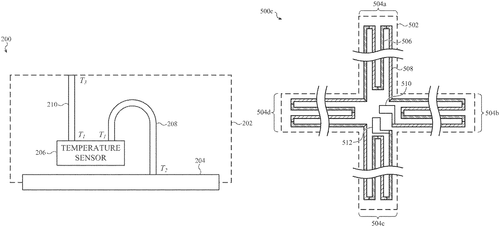
In a recent patent application, Apple Inc. has outlined a new temperature sensing system that could potentially be incorporated into their future electronic devices. The system features a temperature sensor and a differential temperature probe, both enclosed within the device's housing. What sets this invention apart from existing temperature sensing technologies is the inclusion of a flexible substrate that defines two ends of the differential temperature probe. The first end is thermally coupled to the temperature sensor, while the second end is thermally coupled to a surface, volume, or component of the electronic device. The probe itself is an in-plane thermopile, comprising a series of thermocouples that extend from the first end to the second end. By measuring the temperature at the sensor as a first measured temperature, and correlating the voltage difference across the leads of the differential temperature probe to the differential temperature relative to the first measured temperature, Apple's system achieves a second measured temperature. This second measured temperature quantifies the temperature of the second end of the probe. This innovation, if successfully implemented, could have various potential applications. Imagine a scenario where your iPh. one or MacBo. ok can accurately determine the temperature of its internal components, alerting you if it is at risk of overheating. This could prevent potential damage and enhance overall device longevity. Additionally, this technology could be utilized in various smart home devices to optimize temperature control. As exciting as this patent may be, it's important to remember that not all patented ideas make it into actual products. It remains to be seen whether Apple will incorporate this temperature sensing system into their future devices or whether it will be shelved in the realm of theoretical concepts. What are your thoughts on this potential invention by Apple? Do you feel that temperature sensing systems would be a valuable addition to electronic devices? Share your opinions in the comments below!
This text describes an electronic device that includes a temperature sensing system, including a temperature sensor and a differential temperature probe. The differential temperature probe includes a flexible substrate defining two ends. A first end is thermally coupled to the temperature sensor and a second end is thermally coupled to a surface, volume, or component of the electronic device. The temperature probe is an in-plane thermopile including a series-coupled set of thermocouples extending from the first end to the second end. A temperature measured at the temperature sensor can be a first measured temperature and a voltage difference across leads of the differential Temperature probe can be correlated to a differential temperate relative to the first measured temparature. A sum of the differential temperate and the first measured temperate is a second measurment temperate, quantifyinga temparature ofthe secon dendofdifferentialtemperatureprobe
US Patent 11781919
Apple Inc.
An Electronic Device That Detects If An Object Is Animating Or Inanimate Could Help Improve Wireless Performance
What is this invention?
Electronic devices with non-static object detection
An electronic device with a VSWR,
Measures the RF signals you see.
A detection of animate or inanimate,
Is used to set power levels that be.
To ensure safety and performance it must comply,
Maximizing wireless capability!
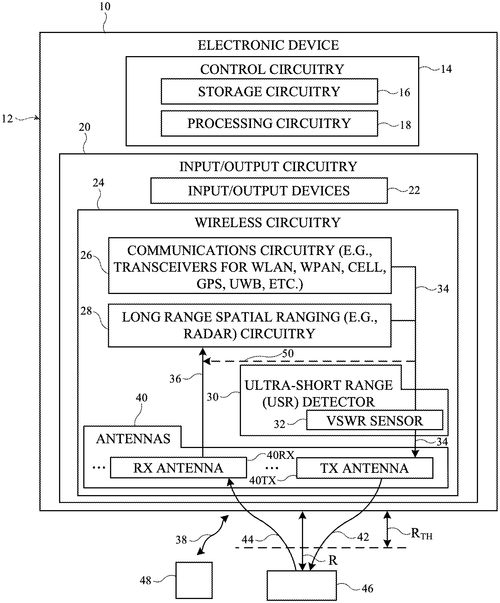
In a recent patent application, Apple Inc. has revealed an interesting innovation that could potentially improve wireless performance in electronic devices while ensuring compliance with regulatory limits on radio-frequency energy exposure. The patent describes the integration of a voltage standing wave ratio (VSWR) sensor within an electronic device, specifically along the radio-frequency transmission line between a signal generator and an antenna. The VSWR sensor would be capable of collecting VSWR measurements from radio-frequency signals transmitted by the signal generator over the transmission line. By monitoring the variation in these measurements over time, the control circuitry within the device would be able to determine whether there is an external object in the vicinity of the antenna, and whether that object is considered animate or inanimate. If an animate object is detected, such as a human, the control circuitry would then lower the maximum transmit power level of the antenna. On the other hand, if an inanimate object is detected, the maximum transmit power level can be maintained or even increased. The goal here is to optimize wireless performance while simultaneously adhering to regulations regarding radio-frequency energy exposure. While this patent showcases an interesting concept, it's important to keep in mind that not all patented inventions actually make it into commercial products. It remains to be seen how Apple will leverage this technology and whether it will be implemented in future devices. In terms of potential uses, a device incorporating this technology could automatically adjust its power levels when used in different environments. For example, imagine a smartphone that reduces its transmit power when it detects that it is in close proximity to the user's head, thus minimizing radio-frequency exposure during phone calls. Conversely, it could increase power levels when the phone is placed far away from the user, ensuring stronger and more reliable wireless connections. Of course, it's always fascinating to see how technology evolves, and this patent definitely invites speculation about the possibilities it presents. However, it's important to temper our excitement with a dose of pragmatism until we see whether and how Apple implements this invention. What are your thoughts on this patent? Do you see potential applications beyond wireless performance and compliance? Let us know in the comments below!
An electronic device may include a voltage standing wave ratio (VSWR) sensor disposed along a radio-frequency transmission line between a signal generator and an antenna. The VSWR sensor may gather VSWR measurements from radio-frequency signals transmitted by the signal generator over the transmission line. Control circuitry may identify a variation in the VSWR measurements over time and may compare the variation to a threshold value to determine whether an external object in the vicinity of the antenna is animate or inanimate. When it is determined that an external object is animate, control circuitry may reduce the maximum transmit power level of the antenna. When it is determined that an external object is not animate, control circuitry may maintain or increase the maximum transmit power level of the antenna. This may serve to maximize wireless performance of the electronic device while also ensuring compliance with regulatory limits on radio-frequency energy exposure
US Patent 11782151
Apple Inc.
Lenticular Display May Enable More Curvature for Stereoscopic Viewing
What is this invention?
Optical film arrangements for electronic device displays
A lenticular display, with convex curvature
Had stereoscopic zones and non-stereoscopic too
To reduce crosstalk they had a louver film
That had transparent parts and opaque walls to fill 'em
The viewing was great, the results were surefire!
The latest patent filed by Apple Inc. has the potential to revolutionize the way we experience displays. With a focus on stereoscopic viewing, this patent describes the creation of a lenticular display with convex curvature. By incorporating a lenticular lens film with lenses that span the length of the display, users will be able to view content in a three-dimensional manner, adding depth and immersion to their visual experience. One of the key challenges in creating a curved lenticular display is maintaining satisfactory stereoscopic performance. To overcome this, the patent suggests incorporating both stereoscopic and non-stereoscopic zones into the display. The central stereoscopic zone is sandwiched between two non-stereoscopic zones that have a higher curvature. This design aims to optimize both the curvature and stereoscopic quality, ensuring an impressive visual experience. Crosstalk, a common issue in lenticular displays where the images from different perspectives overlap, is also addressed in this patent. Apple proposes using a louver film, consisting of transparent portions separated by opaque walls, to control the emission angle of light from the display. By reducing crosstalk, this technology can greatly improve the overall clarity and precision of the displayed images. While this patent demonstrates Apple's commitment to pushing the boundaries of display technology, it is important to note that not all patented inventions become commercially available products. Companies file patents to establish their intellectual property and explore innovative possibilities. As consumers, we can only hope that Apple chooses to develop this technology into a tangible product. If realized, a curved lenticular display with improved stereoscopic performance could be a game-changer for various industries. Imagine watching movies or playing video games with an enhanced sense of depth. Furthermore, the applications of this technology could extend beyond entertainment, potentially revolutionizing fields such as medicine, education, and design. But what are your thoughts on this patent? Do you think Apple will bring this lenticular display technology to the masses? How would you envision using such a display in your daily life? Share your opinions and ideas in the comments below.
A lenticular display may be formed with convex curvature. The lenticular lens film may have lenticular lenses that extend across the length of the display. The lenticular lenses may be configured to enable stereoscopic viewing of the display. To ensure satisfactory stereoscopic display performance, the display may have stereoscopic zones and non-stereoscopic zones. A central stereoscopic zone may be interposed between first and second non-stereoscopic zones. The non-stereoscopic zones may have more curvature than the stereoscopic zone. To prevent crosstalk within the lenticular display, a louver film may be incorporated into the display. The louver film may have a plurality of transparent portions separated by opaque walls. The opaque walls control the emission angle of light from the display, reducing crosstalk.
US Patent 11782190
Apple Inc.
A Folded Telephoto Lens System That Delivers Quality Performance and High Image Resolution in a Small Form Factor Camera
What is this invention?
Folded telephoto camera lens system
A telephoto lens system was made
With multiple lenses and a light path that swayed
The image plane would be formed
By one or more elements aspheric normed
A small form factor camera's what they'll convey
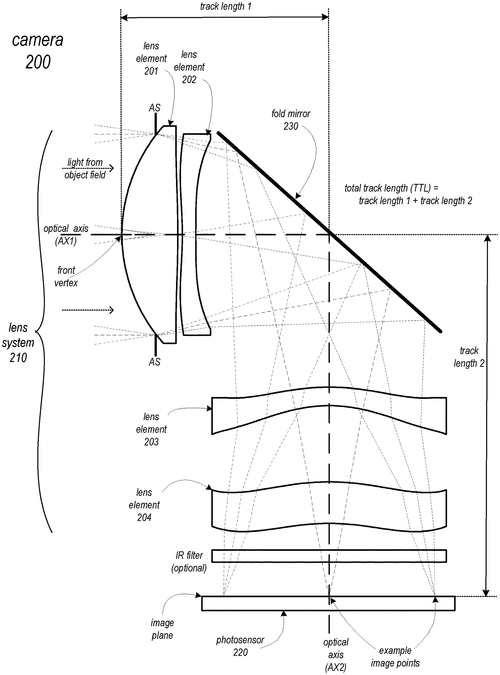
Apple Inc. has recently filed a patent for a folded telephoto lens system that promises to pack high-quality optical performance and high image resolution into a small form factor camera. The patent describes a system consisting of multiple lenses with refractive power and a light path folding element. According to the patent, light entering the camera passes through lens(es) on a first path and is then refracted to the folding element, which changes the direction of the light onto a second path. From there, the light passes through lens(es) that further refract it to form an image plane at a photosensor. At least one surface of the lens elements may be aspheric, enhancing the optical performance. One of the key features highlighted in the patent is the total track length (TTL) of the lens system, which is stated to be 14.0 mm or less. This compact design is aimed at achieving a small form factor camera without compromising image quality. Additionally, the lens system is configured so that the telephoto ratio (TTL/f) is less than or equal to 1.0, further ensuring optimal performance. While the patent lays out the technical details of this folded telephoto lens system, it is important to note that patents do not guarantee the development or release of a product. Apple being a leading player in the smartphone industry, it is certainly intriguing to see them exploring advancements in optics. However, it remains to be seen if and when this technology will be incorporated into their future devices. If this folded telephoto lens system were to make its way into a smartphone, it could potentially revolutionize mobile photography. It may allow for improved zoom capabilities, better low-light performance, and overall enhanced image quality. As the competition heats up in the smartphone camera space, advancements like this could give Apple an edge over its rivals. As we eagerly wait to see what Apple has in store for its future products, what features would you like to see in the next generation of smartphone cameras? Share your thoughts and ideas in the comments below.
This document describes a folded telephoto lens system that includes multiple lenses with refractive power and a light path folding element. The light entering the camera through lens(es) on a first path is refracted to the folding element, which changes direction of the light on to a second path with lens(es) that refract the light to form an image plane at a photosensor. At least one of the object side and image side surfaces of at least one of the lens elements may be aspheric. The total track length (TTL) of the lens system may be 14.0 mm or less, and the lens system may be configured so that the telephoto ratio (TTL/f) is less than or equal to 1.0. Materials, radii of curvature, shapes, sizes, spacing, and aspheric coefficients of the optical elements may be selected to achieve quality optical performance and high image resolution in a small form factor camera.
US Patent 11782240
Apple Inc.
Device Hides Burn-In, Power Consumption Issues with Eye Monitoring
What is this invention?
Electronic devices with display operation based on eye activity
A device of electronic kind
With display to show us what we find
It's eye monitoring system so neat
Detects saccades and blinks, can't be beat
To reduce burn-in and power consumption, it's a treat!
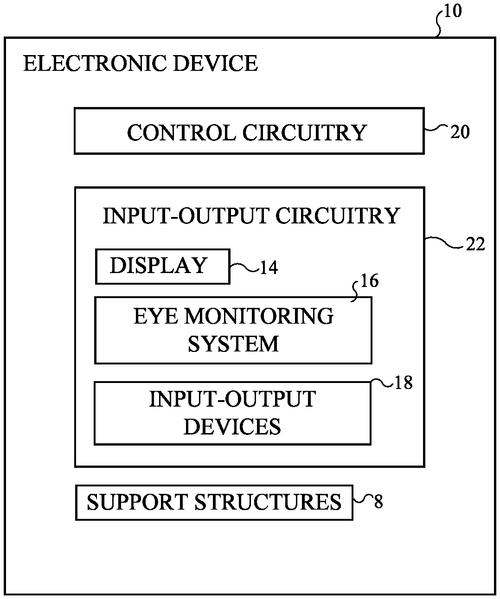
Apple Inc. has recently filed a patent for an intriguing new invention that could revolutionize the way we interact with electronic devices. The patent describes an electronic device with a display that could be supported by head-mounted structures, similar to virtual reality headsets. What sets this invention apart is the integration of an eye monitoring system that detects eye saccades and blinks. The eye monitoring system, combined with control circuitry within the device, allows for coordinated operation of the display with periods of suppressed visual sensitivity associated with eye movements. Essentially, the device would make adjustments to the display and image content during these moments when our vision is momentarily impaired. This could be achieved by modifying certain display circuitry or altering the displayed images in a way that hides potentially visually intrusive changes from the user. The potential uses for this technology are wide-ranging. For instance, it could greatly reduce burn-in effects commonly experienced with OLED displays, where static content can leave a permanent mark on the screen. By making adjustments during eye saccades, the device could minimize the risk of burn-in and prolong the display's lifespan. Moreover, this eye monitoring system could also contribute to a significant reduction in power consumption. By optimizing the display's operation during periods of suppressed visual sensitivity, the device could conserve energy and improve overall battery life. While Apple's patent certainly showcases the innovative thinking of their engineers, it's important to keep in mind that not every patent leads to a tangible product. The tech industry is constantly filled with exciting concepts and ideas, but many never make it past the drawing board. However, if Apple were to develop this invention into a consumer product, it could potentially revolutionize the way we use our electronics. One can't help but wonder how this technology might be integrated into virtual reality headsets or augmented reality glasses, or how it could enhance the user experience for gaming or immersive media consumption. Could this invention mark the next leap forward in display technology? We'd love to hear your thoughts and speculations in the comments below.
The electronic device may have a display for displaying image content. Head-mounted support structures in the device may be used to support the display. The electronic device may have an eye monitoring system that detects eye saccades and eye blinks. Control circuitry in the electronic device may coordinate operation of the display with periods of suppressed visual sensitivity that are associated with the saccades and blinks. By making adjustments to display circuitry and image content during periods of suppressed visual sensitivity, potentially visually obtrusive changes to displayed images can be hidden from a user of the electronic device. Adjustments to display operation may help reduce burn-in effects, may help reduce power consumption, and may otherwise improve device performance.
US Patent 11782503
Google LLC
Detecting Changes in Motion with Sensor Data
What is this invention?
Systems and methods for managing motion detection of an electronic device, and associated electronic devices
An electronic device was set
To detect a change in motion, yet
It stored the data first,
Then ran an algorithm to quench its thirst.
If more motion is detected then it will adjust!
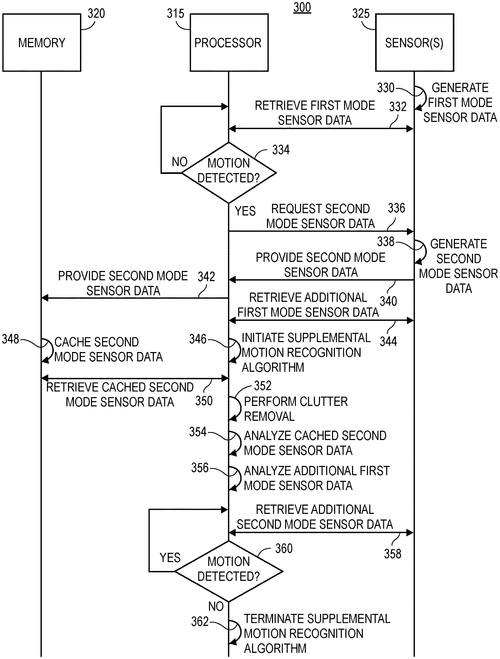
Google LLC has recently filed a patent for a new technology that aims to revolutionize the operation of sensors in electronic devices. The patent describes a system wherein an electronic device can detect a change in motion using sensor data and then analyze the cached data to manage the operation of a supplemental algorithm. While the patent does not explicitly mention any specific products, it opens up exciting possibilities for various electronic devices such as smartphones, tablets, or even wearable gadgets. Imagine a smartphone that can automatically adjust its camera settings based on the user's movement, or a fitness tracker that can accurately track your movements and adjust its algorithms accordingly. This invention certainly seems promising, especially in the world of increasingly advanced technologies. However, it's important to note that filing a patent does not necessarily mean that it will translate into a real product. Many patent filings never make it beyond the conceptual stage. It will be fascinating to see if Google can develop this technology further and integrate it into their existing devices or if it will remain just an idea on paper. Competitors in the market might already have similar technologies or could be working on similar ideas. Companies like Apple, Samsung, or Fitbit could potentially be developing their own approaches to enhancing the performance of sensors in electronic devices. It will be interesting to see how this technology evolves and if it can offer a competitive advantage over existing products. In conclusion, Google's patent for managing the operation of sensors in electronic devices presents an exciting opportunity for innovation. Its potential applications and the competition in the market make it an intriguing development to watch. Will this patent become a reality and transform the way we interact with our devices? What other potential uses can you envision for this technology? Let us know your thoughts in the comments below.
Embodiments are provided for managing the operation of sensors in an electronic device. According to certain aspects, the electronic device may detect a change in motion from an initial set of sensor data generated by a sensor(s). A memory cache may store the initial set of sensor data or additional sensor data generated by the sensor(s). The electronic device may initiate a supplemental algorithm that analyzes the cached data. Based on the analysis of the cached data and whether the change in motion is confirmed or whether additional motion is detected, the electronic device may manage (e.g., adjust) one or more settings associated with the supplemental algorithm.
US Patent 11782149
Google LLC
Narrow Bezels = More Space on Display
What is this invention?
Uniformly narrow display bezels in portable electronic devices
A device with a narrow display bezel,
Was made of a polyhedral cover and chamfered peal.
The top face was angled at one to eighty nine,
So the opaque border remained unseen.
And it's design sure did give its users quite a thrill!
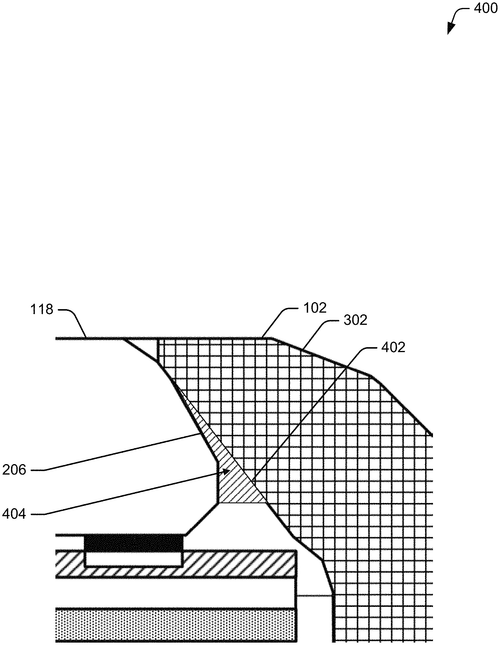
In Google's latest patent, they propose a solution to the age-old problem of thick display bezels on portable electronic devices. This document outlines innovative systems and techniques to achieve uniformly narrow display bezels, giving users an immersive viewing experience. The patent suggests that a portable electronic device, such as a smartphone or tablet, would feature a housing that houses a display panel stack. This stack includes a chamfered, polyhedral cover layer bonded to the top of the display module. The cover layer, with a large chamfer between its top face and side face, defines a chamfered face that extends the perimeter of the cover layer. What makes this invention interesting is the ability to angle the chamfered face at any degree between one and eighty-nine degrees to a horizontal plane defined by the top face. This allows for a front-facing portion, which can be adhered to a parallel or subparallel interior face of the housing. The result? An imperceptible opaque border added to the face opposite the top face. If Google successfully implements this patent, it could revolutionize the design of portable electronic devices, giving them a sleek and modern aesthetic. Users would benefit from increased screen real estate, as the display bezels would be significantly reduced. This could enhance the overall user experience and provide a more immersive feel when interacting with the device. Although this patent sounds promising, it's important to remember that not all patented inventions become actual products. While it's exciting to envision a future where our devices have almost bezel-less displays, we'll have to wait and see if Google decides to turn this concept into a tangible consumer product. In light of this potential development, I'd love to hear from you, the readers. What are your thoughts on the future of display bezels? Do you think users place too much importance on bezel design, or are there practical benefits to having narrower bezels? Let us know in the comments below.
This document describes systems and techniques directed at uniformly narrow display bezels in portable electronic devices. In aspects, a portable electronic device includes a housing that houses a display panel stack having a chamfered, polyhedral cover layer bonded to a top of a display module. The cover layer may include a large chamfer between a top face and side face, defining a chamfered face extending the perimeter of the cover layer. The chamfered face may be angled any number of degrees in a range from one to eighty-nine degrees to horizontal plane defined by the top face of the cover layer, such that the chamfered face possesses front-facing portion. The chamfered face may be adhered to parallel or subparallel interior surface of the housing. In such configuration, an opaque border added to opposite facing edge of topface may be imperceptible to user resulting in uniformly narrow display bezels
US Patent 11782483
Google LLC
The System That Will Save Your Battery
What is this invention?
Smart context subsampling on-device system
A system for intelligent sampling,
To reduce battery usage and keep it from draining.
ML used to optimize the data upload,
So that metrics are always on the up.
The device conditions dictate the policy,
Which helps with this task quite nicely!
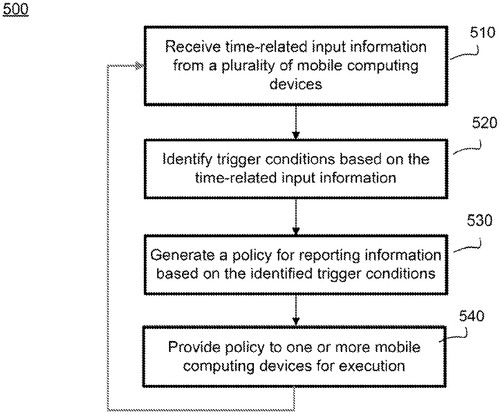
In a recent patent filing, Google LLC has outlined a system that aims to intelligently sample and upload information, such as location and activities, from a device. The technology behind this system utilizes machine learning algorithms to optimize the sampling and uploading process, reducing battery usage while maintaining or even improving the quality of the reported metrics. This invention addresses a common problem faced by users of location-based services – the drain on battery life caused by constant data collection. With the use of machine learning, Google's system could potentially determine the optimum scanning and upload rates based on various conditions within the device, effectively balancing the need for accurate information with the need to conserve battery power. Although the patent filing provides an interesting glimpse into the future of data collection methods, it's important to note that not all patented technologies eventually become products. Google's competitors, such as Apple and Microsoft, already offer similar services that sample user information, albeit with different methods. It remains to be seen if Google will implement this particular system or if it will remain an idea captured in a patent filing. The potential applications for such an intelligent sampling system are vast. Imagine a future where smartphones are able to automatically detect the user's current activity, such as walking, running, or driving, and adjust the frequency of data collection accordingly. This could lead to more accurate mapping and location-based services, as well as improved personalization of device features and applications. As always, we'd love to hear your thoughts on this innovation in the comments below. Do you think this intelligent sampling system could be a game-changer for location-based services, or is it just another patent that may never see the light of day?
The present disclosure provides a system for intelligently sampling information, such as location, activities, etc. on device. Sampling and uploading of background context is optimized using machine learning, such that battery usage is reduced, and quality of metrics based on the reported information is maintained or improved. A policy is generated based on the machine learning, the policy dictating how scanning and upload rates should change in response to conditions on the device.
US Patent 11782496
Google LLC
User-Selectable Option Keeps User Device Presentation Modes Straight
What is this invention?
Contextual triggering of assistive functions
A user device was in the mix
To present content with a few quick clicks
The mode could be changed
And tailored arranged
For each user's individual fix.
In an intriguing patent filed by Google LLC, a new method is described that could potentially revolutionize the way we interact with our user devices. The patent outlines a system that, based on the user's current state, provides a user-selectable option to switch to a different presentation mode. This means that while a user is engaged in the first presentation mode, the system would gather information about the user's state and offer an alternative presentation mode if deemed suitable. While the patent does not specifically mention any competitor's products, it's hard not to draw parallels with existing devices that offer different presentation modes. For instance, Microsoft's Surface line of devices allows users to switch between tablet and laptop mode, adapting to various user needs. If Google were to implement this patent into a future product, it could potentially challenge similar offerings in the market. The potential uses for a system like this are exciting and varied. Imagine, for example, a user device that recognizes the user's fatigue or stress levels and automatically suggests a more relaxed presentation mode with larger text or softer colors. Or perhaps a device that adapts the presentation mode based on the user's physical environment, like switching to a hands-free mode when it detects the user is in a moving vehicle. However, it's important to remember that patents are not guarantees of future products. They often represent ideas and technologies that may or may not make their way into consumer products. While the concept behind this patent is intriguing, it remains to be seen if Google will actually bring it to life. In the comments below, we would love to hear your thoughts on this patent. Do you think a user device that adapts its presentation mode based on the user's state would be a valuable addition to the market? How would you envision using such a feature in your daily life? Let us know!
The text describes a method for presenting content to a user on a user device, where the presentation mode can be changed based on the current state of the user. When a user selects an option to use a different presentation mode, the content is presented in that mode. This allows for more customized and tailored presentations for individual users.
US Patent 11782569
Google LLC
New Playlist Interface Allows Users to Add Interstitials After Media Items
What is this invention?
Cloud-based tool for creating video interstitials
A playlist interface was provided,
With a selectable indicator inside.
When the user pressed it to start,
The UI elements did impart
Configuration parameters for an interstitial ride!
Google's latest patent application seeks to revolutionize playlist creation with the addition of interstitials, according to a recent disclosure. The patent describes a playlist interface that allows users to select a specific indicator after a media item, indicating that an interstitial, or supplemental content, will be added after that first item. Users can then specify the configuration parameters for the interstitial, such as its content and placement within the playlist. The interstitial is created based on these parameters and can be added before or after any of the media items in the playlist. On the surface, this invention may seem like a minor improvement to playlist management, but it opens up interesting possibilities for users seeking to enhance their audio or video experiences. Imagine music playlists interrupted by short artist interviews, behind-the-scenes footage, or even interactive advertisements. Similarly, video playlists could feature bonus scenes, pop-up trivia, or educational segments. But before getting too excited, it's important to note that a patent application does not guarantee a commercial product. While Google's track record in innovation is impressive, it remains to be seen how and if this particular technology will be integrated into their existing products or offered as a standalone service. Competitors like Spotify and Apple Music may already have similar functionalities in their platforms, such as playlists with limited interstitial content. However, the specificity and customizable nature of Google's proposed invention may give it an edge, depending on the implementation. Considering the increasing popularity of streaming services and the growing demand for personalized content consumption, the concept behind Google's patent application certainly holds promise. Whether it will ultimately materialize as a user-friendly feature remains to be seen. Readers, what are your thoughts on the potential integration of interstitials in playlists? Do you find the idea innovative and appealing, or do you prefer uninterrupted and seamless audio or video experiences? Share your opinions in the comments below.
A playlist interface is provided for display on a user device, the playlist interface comprising a selectable indicator located after a first media item in the playlist, the selectable indicator presented in the playlist interface after the first media item to indicate that, upon selection, a second media item is to be added after the first media item in the playlist. Upon a user selection of the selectable indicator located after the first media item in the playlist interface, a plurality of user interface (UI) elements are caused to be presented to allow a user of the user device to specify configuration parameters for the interstitial being added to be added tothe playlist. User input is received for at least a subset of UI elements to specify configuration parameters for an interstitial being created based on those configuration parameters. The interstitial is created based on those configuration parameters and is supplemental content that will be added before or after one of a plurality of files of a plurality ofmedia items in the playlist.
US Patent 11782585
Amazon Technologies, Inc.
New Method Identifies Single-Entry-Single-Exit Subgraphs in Computational Dataflow Graphs
What is this invention?
Reconfigurable neural network processing based on subgraph recognition
A method for accelerating dataflow
Received codes to represent a graph so
It traversed the nodes, found SESE subgraphs
Then merged each operator with its math staffs
The hardware then executed instructions on behalf of you.
In a recent patent application, Amazon Technologies, Inc. has outlined a method for optimizing the execution of computational dataflow graphs. The proposed method includes receiving input codes that represent a computational dataflow graph, identifying single-entry-single-exit (SESE) subgraphs within the graph, and determining a merged operator for each SESE subgraph. The invention aims to generate executable instructions for the computational dataflow graph to be executed by a hardware accelerator with multiple execution units. While the patent application offers intriguing possibilities for optimizing computational processes, it is important to note that not all patented technologies make it to market as fully realized products. This invention, if developed, could potentially enhance the efficiency of data processing and accelerate the execution of complex tasks. Competitor products in this space, such as Intel's Movidius Neural Compute Stick and Google's Tensor Processing Unit, show that there is a growing demand for hardware accelerators tailored to machine learning and artificial intelligence applications. If Amazon were to successfully transform this patent into a tangible product, it could have a significant impact on the AI and data analysis landscape. The potential applications for such a technology are vast. It could improve the speed and performance of machine learning algorithms, enable more efficient data processing in cloud computing systems, and enhance the capabilities of autonomous systems like self-driving cars or drones. However, it's worth considering the challenges that may arise during implementation. The integration of complex hardware accelerators into existing infrastructure can be a daunting task. Compatibility issues, training requirements, and cost considerations could pose significant obstacles to widespread adoption. As we await further updates on the development of this technology, it prompts us to consider the following question: How do you envision the optimization of computational dataflow graphs could impact your field of work or industry? Feel free to share your thoughts in the comments section below.
The text describes a method for accelerating a computational dataflow graph using hardware. The method receives input codes that represent the graph, and traverses the graph to identify single-entry-single-exit (SESE) subgraphs. For each SESE subgraph, the method determines a merged operator. The generated executable instructions are then executed by the hardware accelerator on behalf of the user.
US Patent 11782706
Amazon Technologies, Inc.
Instructions for a Second Address Space Scheduled for Execution from a Second Hardware Thread
What is this invention?
Security vulnerability mitigation using address space co-execution
A processor was built to amaze,
With two address spaces it could raise.
The first thread ran its course,
But then a second source,
Let the processor run with finesse and grace!
In a recent patent filed by Amazon Technologies, Inc., the company details a new innovation that could potentially enhance the performance of processors. The patent describes a method in which instructions are scheduled for execution on different hardware threads, based on the accessibility of different address spaces. In simpler terms, the technology enables a processor to determine whether a particular address space can be accessed by a specific hardware thread before executing the corresponding instructions. This could lead to improved efficiency and speed in processing tasks, as different instructions can be scheduled on hardware threads that have direct access to the required address spaces. While the patent offers an intriguing idea, it is important to note that availability in actual products is uncertain. Often, companies file patents to protect their intellectual property and explore possibilities for future technologies. Competitors in the processor market, such as Intel and AMD, have their own line of processors with advanced functionalities. It remains to be seen if Amazon will develop this concept into a tangible product to compete in this space. If realized, this technology could potentially have various applications. For instance, it could significantly benefit systems with large datasets, such as database servers, where multiple hardware threads could simultaneously access different address spaces for faster data retrieval. Moreover, it might also find utility in virtualization environments, improving the efficiency of virtual machines running on a single physical processor. Keeping in mind the competitive landscape and the companies' varied research interests, it would be interesting to gauge readers' opinions on the significance of this patent. Do you think the concept presents a promising development for processors, or is it just another idea that may never make it into the market? Leave your thoughts in the comments below.
The text describes how the processor can access two different address spaces. First, a first set of instructions is scheduled for execution at a first hardware thread. This instruction set accesses a first address space. Next, before executing the instruction set from the first hardware thread, it is determined that another hardware thread on the processor also has access to a second address space. Finally, based on this determination, the instruction set from the first hardware thread can be executed in conjunction with the instructions from the second hardware thread.
US Patent 11782713
Amazon Technologies, Inc.
Bootstrap Data for SoC Provided in Parallel
What is this invention?
Serial bootstrap
A SoC needs data to bootstrap
But pins can be hard for one to map
Using shift registers galore
Data is received in parallel store
Eliminating complexity, more than a snap!
Amazon Technologies, Inc. has recently filed a patent for a novel approach to provide bootstrap data for computing devices, specifically system on chips (SoC). The patent describes the use of shift registers to receive bits of a bootstrap data sequence in parallel. These bits can then be transmitted to the SoC serially using a single input, eliminating the need for multiple bootstrap pins on the device. This approach addresses a common problem faced by SoCs. , which typically require multiple bootstrap pins to initialize and configure the device. With the use of shift registers, the patent aims to streamline the process by condensing the data transmission into a single input. This not only saves space on the SoC but also eliminates the need to multiplex the pins for use with external devices. While the patent showcases an innovative solution to streamline the bootstrap data process, it is important to note that not all patented ideas translate into tangible products. Competitors in the market, such as Intel and Qualcomm, may have their own approaches to solve similar issues. It remains to be seen whether Amazon Technologies will make this solution a reality and integrate it into their SoCs. or if it will remain an interesting concept confined to patent documents. Potential applications for this technology could be found in various computing devices, including smartphones, tablets, and IoT devices. By simplifying and optimizing the bootstrap data transmission, device manufacturers could potentially enhance the speed and efficiency of their products' initialization process. As with any new patent, it is difficult to predict the exact impact this technology will have on the industry. However, the concept's potential to address a common issue in computing devices sparks curiosity. How do you think this innovative approach to bootstrap data transmission could revolutionize the SoC market? Share your thoughts in the comments below.
This document describes various approaches for providing bootstrap data for a computing device, such as a system on chip. Using one or more shift registers, bits of the sequence of bootstrap data can be received in parallel, seriallyizing the data and providing it to the device using a single input. This approach eliminates the need for multiple bootstrap pins on the SoC and reduces complexity associated with using those pins for other purposes.
US Patent 11782726
Amazon Technologies, Inc.
Your settings, now persistent on your computer!
What is this invention?
Persisting user settings for non-persistent application streaming environments
A streaming app for each user,
It's settings must not be a blur.
The agent will find,
Where to store the file bind,
So preferences won't ever demur.
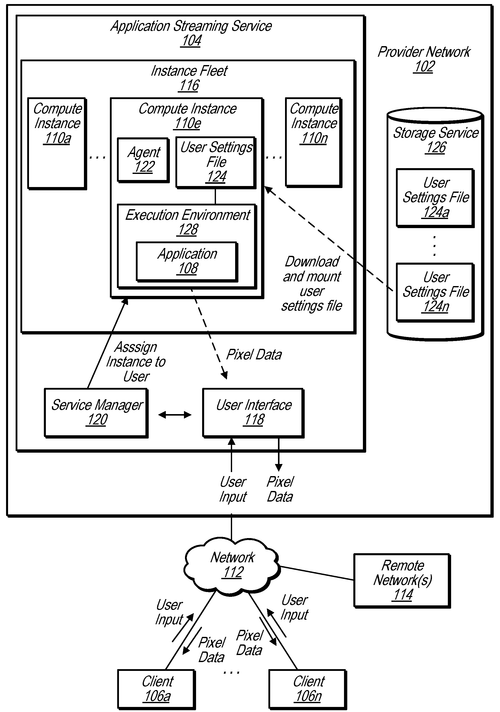
Amazon Technologies, Inc. has recently filed a patent for a rather intriguing technology that aims to solve a common problem faced by users of application streaming services. The patent describes methods, systems, and computer-readable media for persisting user settings for non-persistent application streaming environments. In simple terms, the technology allows an application streaming service to remember and retain the customized settings of individual users, even when they are not using the application. Users often find it frustrating when they have to reconfigure their settings every time they launch a streamed application, but this patent offers a potential solution. According to the patent, an agent provided by a compute instance (a virtual computer) downloads a user settings file from a storage location and mounts it at a specified file system location. This allows the compute instance to execute the application with the user's custom settings. The user settings file is continuously updated as the application is being used and is then uploaded back to the storage location when the session ends. While this technology could potentially enhance the user experience of application streaming services, it remains unclear whether Amazon intends to transform this patent into a product. Furthermore, competition in this space is already fierce, with companies like Google and Microsoft offering their own application streaming services. It would be interesting to see if Amazon can differentiate its offering with this new technology. Looking beyond application streaming services, one can imagine potential applications for this technology in various contexts. For example, it could be utilized in cloud-based work environments, enabling users to seamlessly pick up where they left off on any device without losing their personalized settings. As with most patents, the real-world implementation of this invention is uncertain. So, while the concept is intriguing, it remains to be seen whether Amazon will fully develop and commercialize this technology. What are your thoughts on this patent? Do you use application streaming services, and if so, how would this technology improve your experience? Leave your comments below.
This document describes methods, systems, and computer-readable media for persisting user settings for non-persistent application streaming environments. An application streaming service may receive a selection of an application for a user and assign a compute instance to the user. An agent provided by the compute instance obtains a storage location of a user settings file associated with the user (e.g., based on use of the application during a previous session). The agent downloads the user settings file from the storage location to the compute instance and mounts the user settings file at a file system location associated with an execution environment of the compute instance. The application is executed and the user settings file is updated during use of the application. In response to termination of the session, the agent uploads the updated user settings file to a storage location.
US Patent 11782731
Amazon Technologies, Inc.
Integrated Circuit Regulates Data Flow in Computing System
What is this invention?
Flexible data handling
An integrated circuit, so small and discrete
Can regulate data flow in a computing feat
It receives input data, with size that may vary
Then generates output from the read transaction's query
To store the input data, it has quite a trick
A useful tool for all of computing to pick
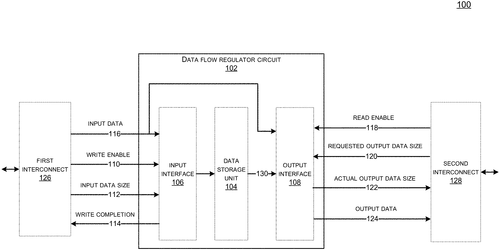
Amazon Technologies, Inc. has recently patented an intriguing integrated circuit that promises to revolutionize data flow regulation in computing systems. This innovative chip boasts the ability to receive input data through a first interface, utilizing a specific bus protocol, and provide output data through a second interface, adhering to a different bus protocol. What makes this invention particularly interesting is its adaptability to handle varying sizes of input and output data, depending on the corresponding protocols. The integrated circuit is designed to receive an input data size for a write transaction via the first interface, allowing for efficient storage of the data in a data storage unit. Furthermore, it can receive a requested data size through the second interface, enabling the provision of output data for a read transaction. To make data transfer even more efficient, the integrated circuit can generate an actual size of the output data based on the requested data size, input data size, and the size of the stored input data. While this patent showcases promising potential in terms of optimizing data flow regulation within computing systems, there are several factors to consider before deeming it a practical solution. Integration of this chip into existing computing systems may require significant modifications, and compatibility with other components needs to be assessed. In terms of competition, there are already various products available that provide similar functions to enhance data flow in computing systems. Companies such as Intel and AMD offer integrated circuits with advanced data management capabilities. Therefore, it will be interesting to see how Amazon's integrated circuit compares and whether it can stand out in the existing market. The potential uses of this technology are vast. From improving data transfer speeds in cloud computing systems to enhancing the efficiency of data-intensive tasks in artificial intelligence and machine learning, the integration of this integrated circuit could undoubtedly bring significant benefits. However, as always, the question remains: Will this patent ultimately lead to the development of a tangible product? What potential barriers may arise during the process, and how might this chip stack up against current competitor offerings? Share your thoughts and insights in the comments below.
An integrated circuit can be used to regulate data flow in a computing system. The integrated circuit can receive input data via a first interface associated with a first type of bus protocol and provide output data via a second interface associated with a second type of bus protocol. Size of the input data and the output data may vary based on the corresponding protocols. The integrated circuit can receive, via the first interface, an input data size for a write transaction to store the input data in a data storage unit. The integrated circuit can also receive a requested data size, via the second interface, to provide the output data for a read transaction. The integrated circuit can also generate an actual size of the output data based on the requested data size, the input data size, and size of the stored inputdata.
US Patent 11782865